Thrombotic Stroke Symptoms and Treatment
A Clotted Danger: Comprehending A Thrombotic Stroke
Stroke falls into two main categories: ischemic and hemorrhagic. Stroke is a leading cause of disability and death globally. The most prevalent kind of ischemic stroke, thrombotic stroke, is the subject of this blog entry. A blood clot that forms in the arteries providing blood to the brain can cause thrombotic stroke, which interrupts critical blood flow and may result in brain damage.
Table of Contents
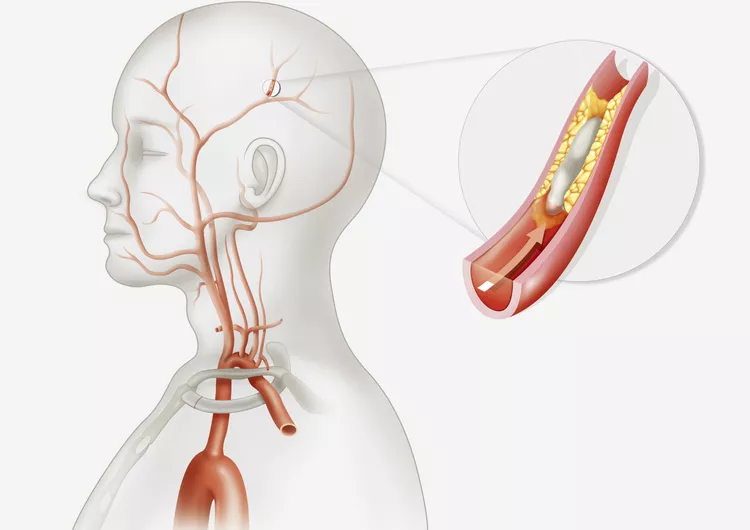
Blood Clot Causing Factor: The Mechanism of Thrombotic Stroke
Thrombotic Stroke Symptoms and Treatment
The brain depends on blood flow to provide it with an uninterrupted supply of nutrients and oxygen. A blood clot that forms in an artery supplying the brain blocks or severely reduces blood flow in thrombotic stroke victims. There are two primary causes of this obstruction:
- Atherosclerosis: This illness is characterized by the accumulation of plaque, a fatty material, inside the arterial walls. Plaque accumulation over time can cause stenosis, or narrowing of the artery, and raise the possibility of clot formation on the roughened surface.
- Other places, blood clots formed: Other areas of the body, particularly the heart or large blood veins, might develop blood clots. A thrombotic stroke can result from a clot that breaks loose and travels through the bloodstream to lodge in a brain artery that has constricted.
Thrombotic Stroke Risk Factors: Who Is More At Risk?
Thrombotic Stroke Symptoms and Treatment
The following variables raise your chance of having a thrombotic stroke:
- High blood pressure: Unchecked hypertension causes plaque accumulation and destroys the walls of blood vessels.
- High cholesterol: An abundance of LDL (bad) cholesterol encourages the buildup of plaque in arteries.
- Smoking: Smoking raises the risk of blood clotting and destroys blood vessels.
- Diabetes: This illness can lead to plaque development and blood vessel damage.
- Atrial fibrillation: An irregular and frequently fast heartbeat linked to a higher risk of cardiac clot formation, which can subsequently spread to the brain, is known as atrial fibrillation.
- Obesity: Being overweight increases the risk of thrombotic stroke, diabetes, and high blood pressure.
- Family history: Your risk is increased if you have a close family who has had a stroke in the past.
- Age: As people age, their risk of thrombotic stroke rises.
Quiet Danger: Identifying Thrombotic Stroke Symptoms
Thrombotic Stroke Symptoms and Treatment
The symptoms of a thrombotic stroke might vary in size and location, usually manifesting quickly. Identifying the warning indicators is essential to getting medical help as soon as possible. To help you recall the main symptoms, here is the acronym FAST:
- F – Drooping of the face: Does one side of the face sag or experience numbness?
- A-Weakness in one arm: Is one arm numb or weak? Is there someone who can equally raise both arms?
- S – Difficulty of speech: Is the speech slurred or hard to understand?
- T-Call emergency services at this time: Make sure to contact emergency services right away if you see any of these indicators!
Other signs and symptoms could be:
- sudden issues with one or both eyes’ eyesight
- lightheadedness or unsteadiness
- intense headache
- Bewilderment or trouble thinking
Recognizing Thrombotic Stroke and Taking Prompt Action
Thrombotic Stroke Symptoms and Treatment
Initiating treatment and reducing brain damage require prompt diagnosis. Typically, a variety of tests are used by medical professionals to detect thrombotic stroke:
- Physical examination: Your reflexes, muscle strength, coordination, and speech will all be evaluated during a neurological exam.
- Tests using brain imaging: Brain injury, obstructions, or bleeding may be shown on an MRI or CT scan.
- Angiography: This imaging modality can identify the precise site of an obstruction by seeing blood flow through the arteries.
Thrombotic Stroke Treatment Approaches: Bringing Blood Flow Back
Thrombotic Stroke Symptoms and Treatment
The main objective of treating thrombotic stroke is to get blood flowing again to the brain as soon as feasible. These are the primary methods of treatment:
- Thrombolytic therapy: Within a certain amount of time, blood clots can be broken up and blood flow restored with the use of medications, commonly referred to as clot busters.
- Endovascular thrombectomy: This is a minimally invasive technique in which the blood clot is removed from the artery using a catheter.
- Medication: Blood pressure and blood thinners are two drugs that can help stop strokes in the future.
- Rehabilitation: Speech, occupational, and physical therapy can assist restore function and help people regain lost abilities.
Thrombotic Stroke Symptoms and Treatment
To maximize recovery outcomes, early intervention is essential. Your chances of recovering lost abilities are better and you are less likely to suffer irreversible brain damage if treatment is started early.
Effects of Thrombotic Stroke in the Long Run: Accepting Recovery
Thrombotic Stroke Symptoms and Treatment
The severity and location of a thrombotic stroke can have a significant impact on its outcomes. While some people make a full recovery, others could struggle in the long run with:
- issues with movement, such as paralysis or weakness
- Speech and language issues
- issues with vision
- Issues with thinking and memory
- Changes in emotions


