Antibiotic Resistance
An antibiotic resistance study in major medical publications has illuminated a growing public health issue in Sub-Saharan Africa. Children in the region are resistant to basic antibiotics at worrisome rates. This highlights the global antibiotic resistance danger and the urgency of action.
Table of Contents
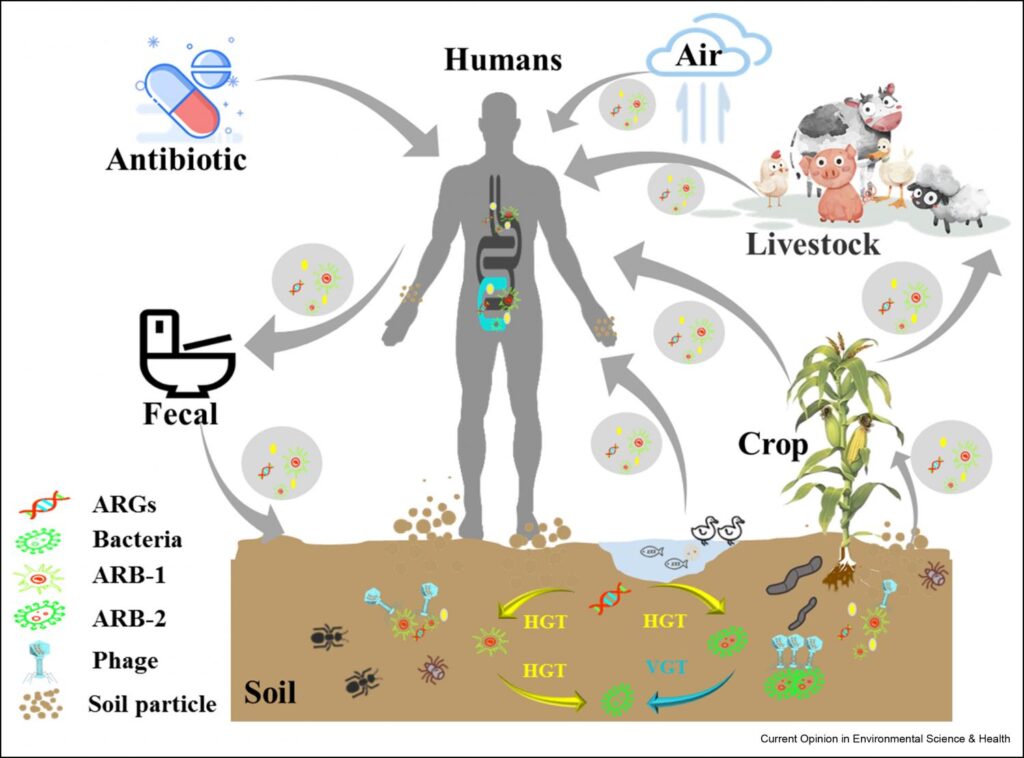
Why Antibiotics Matter
Modern medicine relies on antibiotics. These life-saving medications kill or block bacteria development, helping our bodies fight infections.
Antibiotics are essential for treating pneumonia, sepsis, and safe surgery.
Unfortunately, antibiotic overuse and misuse have caused microorganisms to evolve resistance. Infections are untreatable because “superbugs” are drug-resistant. This resistance is harmful, especially for vulnerable groups like children
Sub-Saharan African studies showed:
- High Prevalence: Many E.coli and Klebsiella bacteria from affected children were antibiotic-resistant.
- Childhood Vulnerability: Children with growing immune systems are more susceptible to illnesses and antibiotic resistance.
- Few Treatment Options: Last-resort medications, which have serious side effects and are more expensive, are needed when first-line antibiotics fail.
A Perfect African Storm
Several factors increase antibiotic resistance in Sub-Saharan Africa:
Few have access to accurate diagnostics, resulting in needless or incorrect antibiotic prescriptions.
- Self-Medication: Overuse of antibiotics is driven by their affordability and accessibility.
- Cleanliness Issues: Bacteria thrive with poor sanitation and hygiene, increasing the risk and frequency of infections and antibiotic use.
- Use of Antibiotics in Livestock Antibiotic use in livestock production can cause bacteria to become resistant and spread to people.
- Beyond Individual Health: Ripple Effect The effects of widespread antibiotic resistance go beyond human health.
How it affects nations:
- Higher Mortality: Untreatable illnesses can kill more people, especially children and the elderly.
- Health Systems Strain: Complex, drug-resistant illnesses strain healthcare resources.
- Economic Stress: Resistant infections and consequences damage national economies.
- A Call to Action: Fight the Resistance
Combating antibiotic resistance needs multiple strategies:
- Strengthening Healthcare Systems: Diagnostics, antibiotic stewardship, and healthcare worker education are essential to improving healthcare systems.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Behavior change requires public education on antibiotic abuse and self-medication.
- Research & Development Investment: Staying ahead requires research into new antibiotics, alternative medicines, and speedy diagnostic techniques.
- Sanitation and hygiene: Improved sanitation and hygiene can greatly reduce antibiotic use.
- Antibiotic Use in Livestock: Stricter antibiotic use laws in animal husbandry can reduce resistance.
- Collective Work: Global Conflict, Local Response
The fight against antibiotic resistance demands global cooperation.
Sharing knowledge, resources, and best practices will help Sub-Saharan Africa address this vital issue. However, it’s a local conflict. Each nation must create and implement comprehensive strategy to handle its difficulties.
The scenario in Sub-Saharan Africa highlights the global antibiotic resistance concern. We can keep these life-saving antibiotics effective by emphasizing antimicrobial stewardship, investing in healthcare infrastructure, and raising awareness.


