Arrhythmias
The Abnormal Heartbeat: Comprehending Arrhythmias
The natural rhythm of your heartbeat guarantees effective blood flow throughout your body. This rhythm is disturbed by commonly referred to as irregular heartbeats. They may result in an irregular, rapid, or sluggish heartbeat. While certain arrhythmias are benign, others may be dangerous medical problems that need to be treated. By elucidating and outlining their various forms, causes, symptoms, and available treatments, this blog post will enable you to comprehend and properly manage this medical issue.
Table of Contents
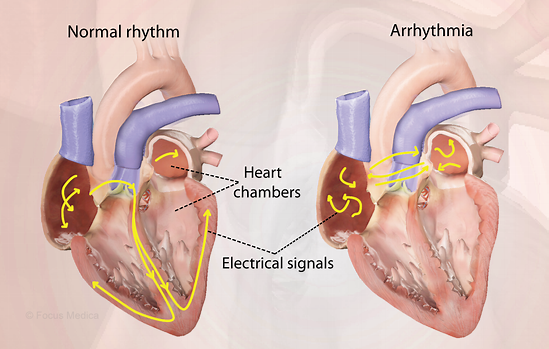
The Heart’s Natural beat: Maintaining the Beat
- Sinus Node: The right atrium contains an inbuilt pacemaker that regulates the heart’s beat.
- Electrical impulses: The sinus node produces electrical impulses that pass through the heart and cause the chambers to contract in unison, effectively pumping blood.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): The electrocardiogram, or ECG, is a test that gauges the electrical activity of the heart and shows the heart rhythm graphically.
The Offbeat Differences: Arrhythmia Types
Based on the source of the irregular electrical signals and how they affect heart rate, arrhythmias can be divided into several categories:
- Tachycardia: A resting heart rate of more than 100 beats per minute (bpm).
- Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT): An elevated heart rate that results from abnormal electrical signals that start above the ventricles (lower chambers).
Ventricular tachycardia (VT): Causes fast, possibly hazardous heartbeats that originate in the ventricles themselves.
Bradycardia: A resting heart rate of less than 60 bpm. - Sinus Bradycardia: This condition may not be dangerous because the sinus node produces slow electrical signals that slow the heart rhythm.
Heart block: A slow or erratic heartbeat is caused by an interruption in the electrical signals that flow between the upper and lower chambers of the heart.
Premature Beats: Abnormally timed extra heartbeats, sometimes referred to as palpitations or skipped beats.
What Causes the Disruption: What Sets Off Arrhythmias
There are several things that might cause arrhythmias:
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Ischemic heart attacks and abnormal electrical impulses are caused by plaque accumulation in the coronary arteries.
- High Blood Pressure: Heart strain and arrhythmias can be caused by persistently elevated blood pressure.
- Heart Attack: Electrical signals may be interfered with if the heart muscle sustains damage.
- Heart Valve Disease: Electrical signals and blood flow can be disrupted by leaking or constricted heart valves.
- Congenital Heart Defects: Birth abnormalities that impact the structure of the heart can raise the risk of arrhythmias.
- Electrolyte imbalances: Heart rhythm can be impacted by imbalances in electrolytes such as potassium and magnesium.
- Thyroid Issues: An overactive or underactive thyroid can affect the rhythm of the heart.
- Medication: Arrhythmias may occur as a side effect of some drugs.
- Stress, Anxiety, and Caffeine: Certain forms of arrhythmias can be aggravated or triggered by stress, anxiety, and caffeine.
- Sleep apnea: This illness can cause irregular sleep patterns and raise the risk of arrhythmias.
The Body’s Reaction: Arrhythmia Symptoms
Arrhythmias can result in a variety of symptoms, however some people may not even notice any. Here are a few typical indicators:
- Palpitations: The sensation of irregular heartbeats, racing, or fluttering in the heart.
- Lightheadedness or dizziness: During an arrhythmia, there may be a reduction in blood supply to the brain.
- Fatigue: The heart’s ineffective pumping may cause you to feel exceptionally exhausted.
- Breathlessness: This is a common occurrence during physical activity, since the heart finds it difficult to supply enough oxygen to the body.
- Chest Pain or Discomfort: Certain arrhythmias might cause this.
- Sweating: Your body may produce chilly sweats as a result of the erratic heartbeat.
Regaining the Beat: Identification and Management of Arrhythmias
To choose the best course of action, it is essential to diagnose the kind and cause of arrhythmia. An ECG, a Holter monitor—a portable device that records cardiac rhythm for 24 to 48 hours—and other tests are frequently used in this. Options for treatment may include:
- Lifestyle modifications: These include eating a heart-healthy diet, controlling stress, and getting adequate sleep. They are frequently the first line of defence.
- Medication: A number of drugs have the ability to control cardiac rhythm.
- Catheter ablation: A minimally invasive technique in which aberrant electrical signals are produced by destroying tissue with catheters.
- Implanted pacemakers and defibrillators: these devices control cardiac rhythm or shock the body with electricity to return it to normal.