COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
The Unwanted Guest: Comprehending Exacerbations of COPD
Breathing difficulties are a hallmark of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), a lung disorder that progresses over time. Even though COPD is a chronic condition, some patients can have exacerbations—also known as flare-ups—when their symptoms get worse for a while. It’s critical to understand the reasons, signs, and treatment options for these exacerbations if you want to keep your health and wellbeing.
Table of Contents
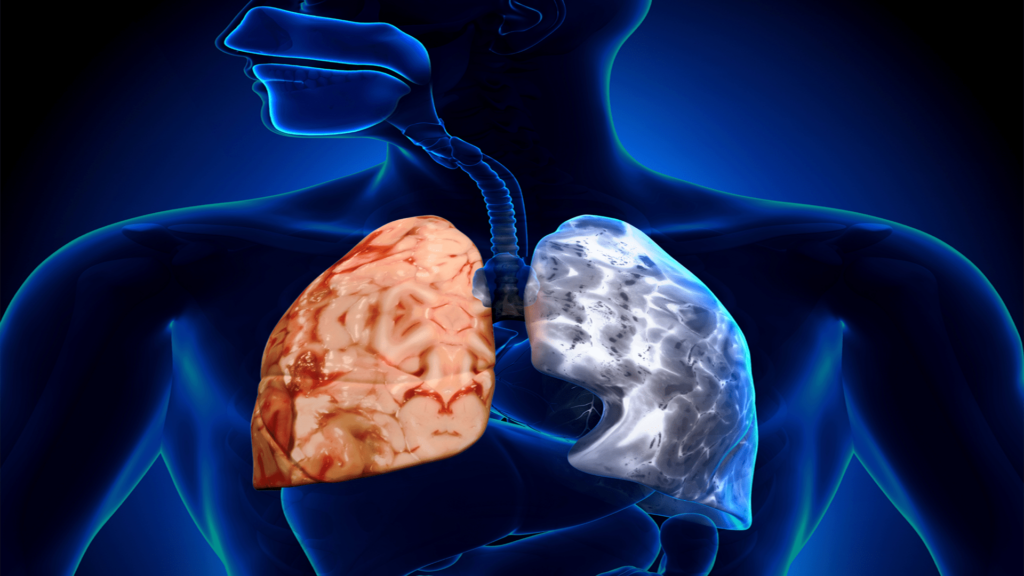
The Reasons for the Outburst: Factors That Induce COPD Severe Episodes
COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
A COPD exacerbation can be brought on by a number of reasons, such as:
- Respiratory Infections: Common causes of respiratory infections include pneumonia, the flu, and colds. Breathing difficulties and increased mucus production are caused by these infections because they aggravate the airways and exacerbate inflammation.
- Exposure to Irritants: Breathing in air pollutants, cigarette smoking, or secondhand smoke can exacerbate the symptoms of COPD and cause an exacerbation.
- Weather Variations: Abrupt shifts in humidity or temperature might make COPD symptoms worse.
- Certain Drugs: Certain drugs, such as beta-blockers (used to treat heart problems), may inadvertently make COPD symptoms worse.
- Stress and Anxiety: People with COPD may experience breathing difficulty and airway tightness as a result of emotional stress.
The Red Flags: How to Spot the Signs of an Exacerbation of COPD
COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
Even though each person’s experience with COPD exacerbations varies, there are a few typical symptoms to be aware of:
- Increased shortness of breath: The most common symptom is increased dyspnea, which can happen even when at rest and is worse when you exert yourself.
- Increased mucus production: You might notice a difference in the quantity, hue, or viscosity of the mucus you cough up.
- Cough changes: Your cough may start to produce more mucus or become more frequent or chronic.
- Wheezing: During an exacerbation, breathing may produce a whistling sound that gets worse.
- Tightness in the chest: A common symptom is a sensation of pressure or discomfort in the chest.
- Fatigue: You can have particularly high levels of fatigue and low energy levels for day-to-day tasks.
- Fever: A respiratory infection that causes the exacerbation may be accompanied by a low-grade fever.
- Modifications in sleep patterns: Breathlessness that makes it difficult to fall asleep is a typical problem.
COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
It’s critical to get medical help right away if you encounter any of these symptoms, especially if they get worse or last longer than a few days. By acting quickly, the exacerbation can be stopped before it gets worse and necessitates hospitalization.
Taking Charge: Handling Severe COPD Episodes
COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
Thankfully, there are methods for controlling exacerbations of COPD:
- Early Identification: It’s critical to identify the early indicators of an exacerbation and to seek medical assistance as soon as possible.
- Medication Modifications: To reduce inflammation and enhance airflow, your doctor may decide to increase the number of inhalers you take.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics will be administered to treat any respiratory infection that is shown to be the trigger.
- Oxygen Therapy: To raise blood oxygen levels and facilitate breathing in extreme situations, more oxygen may be required.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: To assist control symptoms and enhance general health, this program mixes education and exercise training.
- Lifestyle Changes: Reducing stress, avoiding triggers, quitting smoking, and getting enough sleep all help to lower the chance of exacerbations.
Stopping the Unwelcome Visitor: Methods for Reducing Intensities
COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
Take these preventive steps to drastically lower the chance and intensity of COPD exacerbations:
- Vaccinations: Having a yearly immunization against pneumonia and the flu helps avoid respiratory infections, which frequently lead to exacerbations.
- Medication Adherence: Managing COPD and avoiding exacerbations depend on taking your prescription drugs as directed, including inhalers and preventive drugs.
- Quitting smoking: is the single most critical step towards preventing the progression and exacerbations of COPD.
- Healthy Lifestyle: You may greatly enhance your lung health and lower your risk of exacerbations by eating a balanced diet, keeping a healthy weight, and engaging in regular exercise.
COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
You may take charge of your health and lead a more active and satisfying life by being aware of the signs and symptoms of COPD exacerbations and implementing preventive and treatment measures.
Note: This data offers a broad picture of exacerbations of COPD. Seeking individualised advice and treatment from a healthcare expert is advised.



Recent Comments