Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease Progression
Alzheimer’s Disease Stages: A Gradual Decline Advancement
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurological condition that worsens with time and impairs thinking, behaviour, and memory. The illness progresses gradually, and as time goes on, the symptoms get worse. This blog post examines the phases of Alzheimer’s disease development and gives readers a general idea of how the condition develops. It’s crucial to keep in mind that each person will improve at a different rate.
Table of Contents
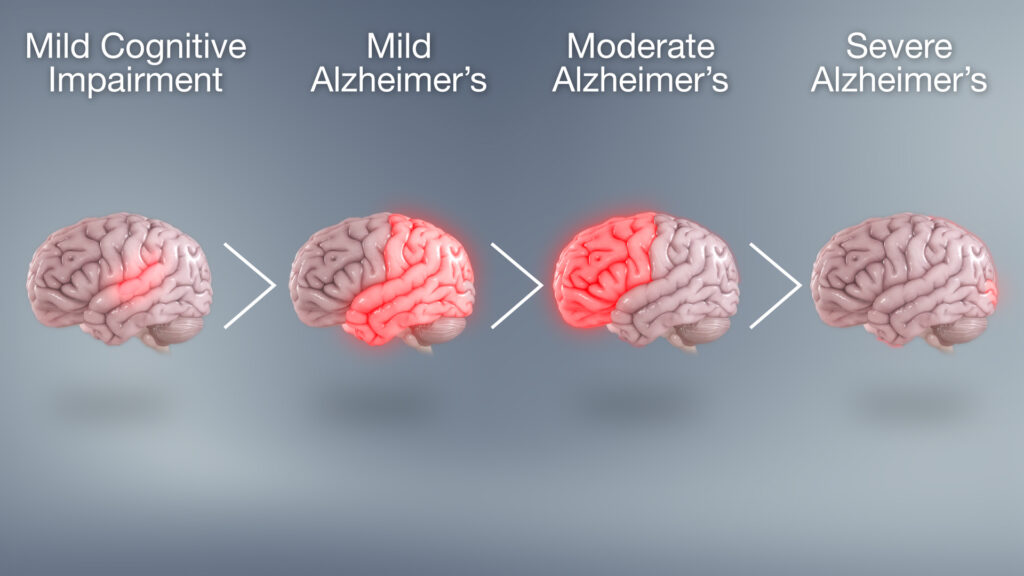
A Spectrum: Mild Cognitive Impairment at the Early Stage
Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease Progression
It can be difficult to recognise mild cognitive impairment (MCI), which is the early stage of Alzheimer’s disease. The mild symptoms could be confused with typical age-related forgetfulness. Here are a few typical indicators:
- Increased forgetfulness: includes losing things, forgetting appointments or names, and having trouble recalling recent discussions.
- A slight deterioration in judgement: would be making dubious choices or finding it difficult to complete routine duties like handling money.
- Language difficulties: Having issues following talks or coming up with the appropriate words.
Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease Progression
While they might not have a big impact on day-to-day living, these symptoms can be bothersome. Still, they should be assessed in order to set a starting point and track any possible advancement.
The Intermediate Phase (Moderate Dementia)
Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease Progression
The symptoms worsen with time and interfere with day-to-day functioning. In the moderate stage, you could see the following:
- Significant memory loss: Difficulty recalling details from the past, private information, and familiar locations.
- Enhanced communication difficulties: include trouble expressing ideas, choosing the wrong words, or having trouble following talks.
- Having trouble managing finances: following multi-step instructions, or organising daily activities are examples of planning and problem-solving challenges.
- Personality and behavioural changes: Withdrawing, distrustful, or displaying mood swings such as depression or anxiety.
Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease Progression
While they could still be able to live alone at this point, people in this stage might require help with everyday duties like meal preparation or medication management.
The Advanced Phase (Alzheimer’s Disease)
Significant loss of independence and substantial cognitive deterioration are hallmarks of the later stages of Alzheimer’s disease. These are a few of the distinguishing features:
- Pervasive memory loss: Inability to identify close ones, forgetting past experiences, and losing sense of place and time.
- Severe communication problems: include trouble understanding or speaking simple directions.
- Unable to carry out daily tasks: Needing help with everything from eating to taking a shower to getting dressed.
- Increased physical problems: include walking difficulties, balance problems, and infection susceptibility.
Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease Progression
Individuals in the later stages need ongoing monitoring and care. They might develop hallucinations, delusions, and behavioural abnormalities that call for medical attention.
Beyond Phases: A Range of Occurrences
Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease Progression
It’s critical to keep in mind that the evolution of Alzheimer’s can vary widely, and that these stages serve as a broad framework. While some people might decrease more quickly than others, others might advance more slowly. Furthermore, each person may experience different symptoms.
Identifying Unusual Presentations
Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease Progression
Alzheimer’s affects individuals differently. Certain people might have unusual symptoms, like:
- Posterior Cortical Atrophy (PCA): This variation mostly affects the brain’s visual regions, leading to issues with vision and spatial orientation.
- Logopenic Progressive Aphasia: The symptoms of Logopenic Progressive Aphasia (LPA) include extreme difficulty finding words and speaking.
Although it can be difficult, early detection of atypical appearances is essential for the right kind of care and assistance.
The Key to Early Diagnosis
Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease Progression
Early diagnosis is crucial, regardless of the precise stage or presentation. It enables people and families to:
- Examine your options for treatment: Although there is no cure, drugs can help control symptoms and enhance quality of life.
- Make a future plan: People with early diagnoses are more equipped to decide on their future care and living situation.
- Seek out support services: To help families deal with the difficulties posed by the illness, resources and support groups are available.
See a medical expert for a thorough assessment if you or a loved one exhibits any worrisome signs.
In Summary: Comprehending the Phases
Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease Progression
Families and individuals dealing with Alzheimer’s disease can benefit from knowing the stages of the disease’s progression. Even though the future may be unknown, getting an early diagnosis and using the resources that are available can provide people and their families the power to manage their condition and choose the best course of action. With information, encouragement, and optimism for improvements in treatment and preventative measures, we can travel this path together.