Types of Diabetes Explained
Uncovering the Spectrum: Comprehending the Various Diabetes Types
A chronic disorder marked by elevated blood sugar levels, diabetes mellitus affects millions of people worldwide. But diabetes is not a single condition; rather, it is a group of conditions with various origins and approaches to treatment. To help you understand the distinctive qualities of the three most prevalent types—Type 1, Type 2, and Gestational Diabetes—this blog post explores each one in detail.
Table of Contents
The Details of Insulin: Comprehending Its Function
Types of Diabetes Explained
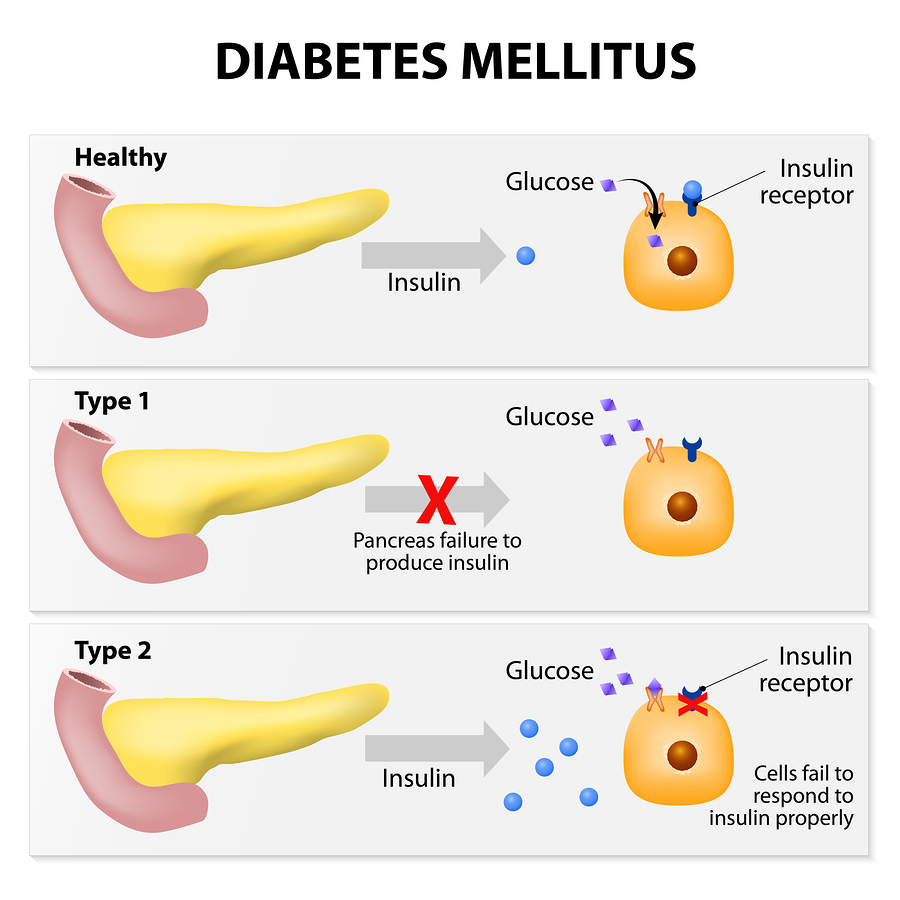
Before we go into particular varieties, let’s review the vital function of insulin. Glucose, the main energy source for cells, is produced by our bodies from meals. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas that opens cells to absorbing glucose from the bloodstream for energy. Insulin keeps blood sugar levels precisely balanced in healthy people.
Type 1 Diabetes: Insufficient Insulin Production in the Body
Types of Diabetes Explained
An autoimmune condition known as type 1 diabetes occurs when the immune system unintentionally targets and kills the pancreatic cells that produce insulin. Insulin production is thereby completely or almost completely inhibited.
- Who It Affects: Although type 1 diabetes can appear at any age, it usually first appears in childhood or early adulthood. There could be a connection between genetics and environment.
- Symptoms include: intense hunger, exhaustion, impaired vision, thirst, frequent urination, sluggish wound healing, and unexplained weight loss.
- Management: Lifelong reliance on insulin shots is essential for those with Type 1 diabetes, as there is no known treatment. For management, blood sugar control, eating a balanced diet, exercising frequently, and other lifestyle changes are crucial.
Type 2 Diabetes: When the Body Isn’t Able to Utilise Insulin Correctly
Types of Diabetes Explained
Over 90% of instances of diabetes are of type 2, which is the most prevalent kind. It results from two primary problems:
- Insulin Resistance: This prevents cells from absorbing glucose by making them less sensitive to insulin.
Inadequate production: of insulin by the pancreas may result in an inability to overcome insulin resistance.
Who is Affected: Family history, obesity, physical inactivity, age, and ethnicity are risk factors. People who have impaired blood sugar management, or prediabetes, are also more vulnerable. - Symptoms: These can include those associated with Type 1 diabetes, but they can also be minor or nonexistent for years. Timely diagnosis is essential.
- Management: Depending on the severity, different management techniques are used. Dietary changes, physical activity, and weight control are frequently the cornerstones. To regulate blood sugar levels, medication—such as injectable insulin or oral medications—may also be required.
Pregnancy and Gestational Diabetes: A Transient Obstacle
Types of Diabetes Explained
Hormonal changes that can impact insulin sensitivity during pregnancy can lead to the development of gestational diabetes. It normally goes away after childbirth, but it raises the chance of Type 2 diabetes in later life.
- Who It Affects: Women with a family history, obesity, or prior risk factors are more likely to develop gestational diabetes during pregnancy, but any woman can develop it.
- Symptoms: Since symptoms are usually absent, frequent prenatal tests are crucial.
- Management: It’s important to monitor blood sugar, make dietary changes, and exercise frequently. There may be instances where medication is required.
The Value of Prompt Diagnosis and Treatment
Types of Diabetes Explained
Whichever kind it is, diabetes must be properly managed and detected early. Living a healthy life with diabetes requires regular blood sugar checks and cooperating with a healthcare provider.
This synopsis offers a fundamental comprehension of the many forms of diabetes. Recall that this information does not replace advice from a medical professional. For an accurate diagnosis and individualised management plans, speak with a healthcare provider if you think you or someone you know may have diabetes.