Carotid Artery Blockage: Carotid Endarterectomy vs. Stenting for Stroke Prevention
Share IT

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.
Categories
Carotid Artery Treatment for Stroke Prevention
Protecting Your Brain: Carotid Artery Stenting vs. Carotid Endarterectomy for Stroke Prevention
Globally, stroke is one of the main causes of disability and mortality. One important risk factor for stroke is narrowing of the carotid arteries, which are the main blood channels that feed the brain with blood. Fortunately, for those with considerable carotid artery stenosis (narrowing), two minimally invasive operations can help avoid strokes: carotid endarterectomy (CEA) and carotid artery stenting (CAS). This blog post explores different procedures, how well they prevent strokes, and things to think about before making a decision.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!Table of Contents
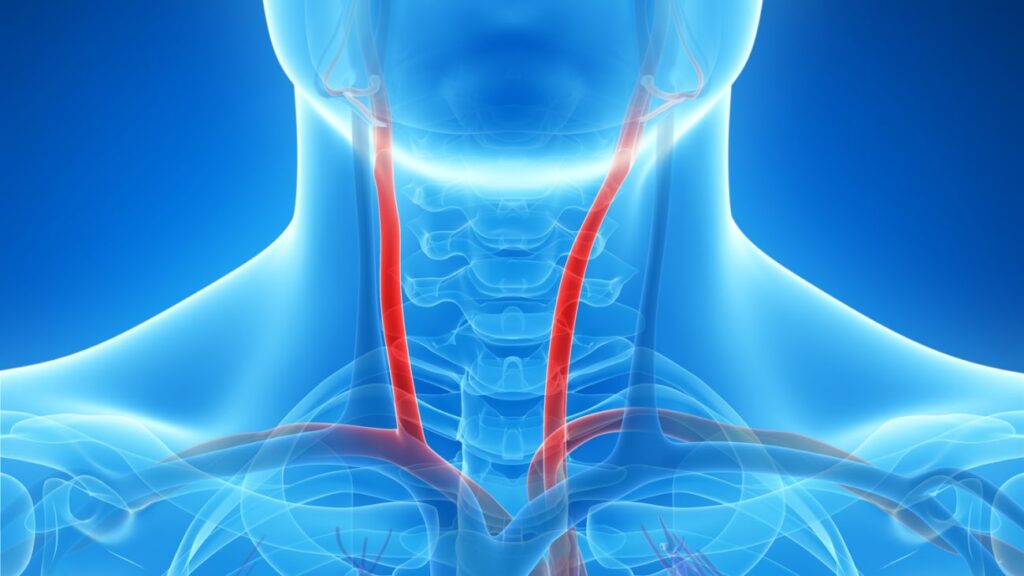
Gratitude Stenosis of the Carotid Artery
Carotid Artery Treatment for Stroke Prevention
The brain receives oxygen-rich blood via the carotid arteries. The carotid arteries may narrow due to atherosclerosis, a buildup of plaque (fatty deposits) inside the artery walls. There is an increased risk of blood clots developing in the narrowed area and going to the brain, which can result in stroke, if this narrowing above a particular threshold (usually 70% or more).
The Operation of a Carotid Endarterectomy (CEA)
Carotid Artery Treatment for Stroke Prevention
A surgical technique called a carotid endarterectomy is used to clear the carotid artery of plaque. This is how the procedure is broken down:
- Anesthesia: To keep you asleep throughout the process, general anesthesia is given.
- Incision: To reach the carotid artery, a neck incision is required.
- Removal of plaque: The artery’s plaque accumulation is carefully removed by the surgeon.
- Closure: If necessary, a patch or graft is used to mend and sew the artery shut.
- Recuperation: After surgery, you’ll usually need to spend a few days in the hospital and then some time recovering at home.
The Operation of Carotid Artery Stenting (CAS)
Carotid Artery Treatment for Stroke Prevention
A stent, a tiny expandable mesh tube, is used in carotid artery stenting, a minimally invasive technique, to enlarge the restricted artery. This is how it works:
- Access: A carotid artery is reached by threading a catheter up through an artery in the groin.
- Balloon angioplasty: To open the restricted artery, a small balloon is inflated inside of it.
- Stent placement: To prevent the artery from narrowing again, a stent is inserted inside the opened section.
- Closure: After the catheter is taken out, the groin access port is sealed.
- Recovery: Compared to CEA, this surgery usually necessitates a shorter hospital stay and a quicker recovery period.
Which Technique Is Best for Me?
Carotid Artery Treatment for Stroke Prevention
The selection between CEA and CAS is contingent upon various criteria, such as:
- Degree of stenosis: CEA may be recommended for extremely significant stenosis levels (over 80%).
- The carotid artery’s anatomy: The type of procedure chosen may depend on the location and form of the obstruction.
- General health of the patient: We’ll take into account bleeding risk and underlying medical issues.
- Experience of the Surgeon: An important consideration is the experience of the surgeon doing either treatment.
Carotid Artery Treatment for Stroke Prevention
Your physician will go over all of these aspects with you in order to decide which course of action is best for your particular circumstances.
Evaluating the Pros and Cons of Every Procedure
Carotid Artery Treatment for Stroke Prevention
When someone has severe carotid artery stenosis, both CEA and CAS can effectively lower their risk of stroke. But every treatment has a unique set of advantages and disadvantages:
Endarterectomy of the carotid:
- Benefits: Because all plaque is removed, this treatment may be more long-lasting for some patients.
- Risks: Compared to CAS, there is a marginally increased chance of complications such as heart attack, stroke, or cranial nerve injury.
Stenting of the Carotid Artery:
- Benefits: include a less intrusive process that requires less time to recuperate from and a possible decreased risk of stroke during the treatment.
- Risks: There is a remote possibility that the stent will move or that the artery could get blocked by a blood clot.
Early Diagnosis and Treatment Are Critical
Carotid artery stenosis must be diagnosed as soon as possible. Seek emergency medical attention if you experience symptoms such as intermittent vision loss in one eye, frequent headaches, or dizziness. The risk of stroke can be greatly decreased with early identification and treatment with either CEA or CAS.
Final Thoughts: Consulting Your Physician
Carotid Artery Treatment for Stroke Prevention
When it comes to stroke prevention in people with severe carotid artery stenosis, both CEA and CAS are useful instruments. Speaking with your doctor about your particular circumstances enables them to suggest the best course of action based on your unique health profile. Recall that maintaining your mental health and preventing a stroke depend on early diagnosis and treatment.

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.






















































Recent Comments