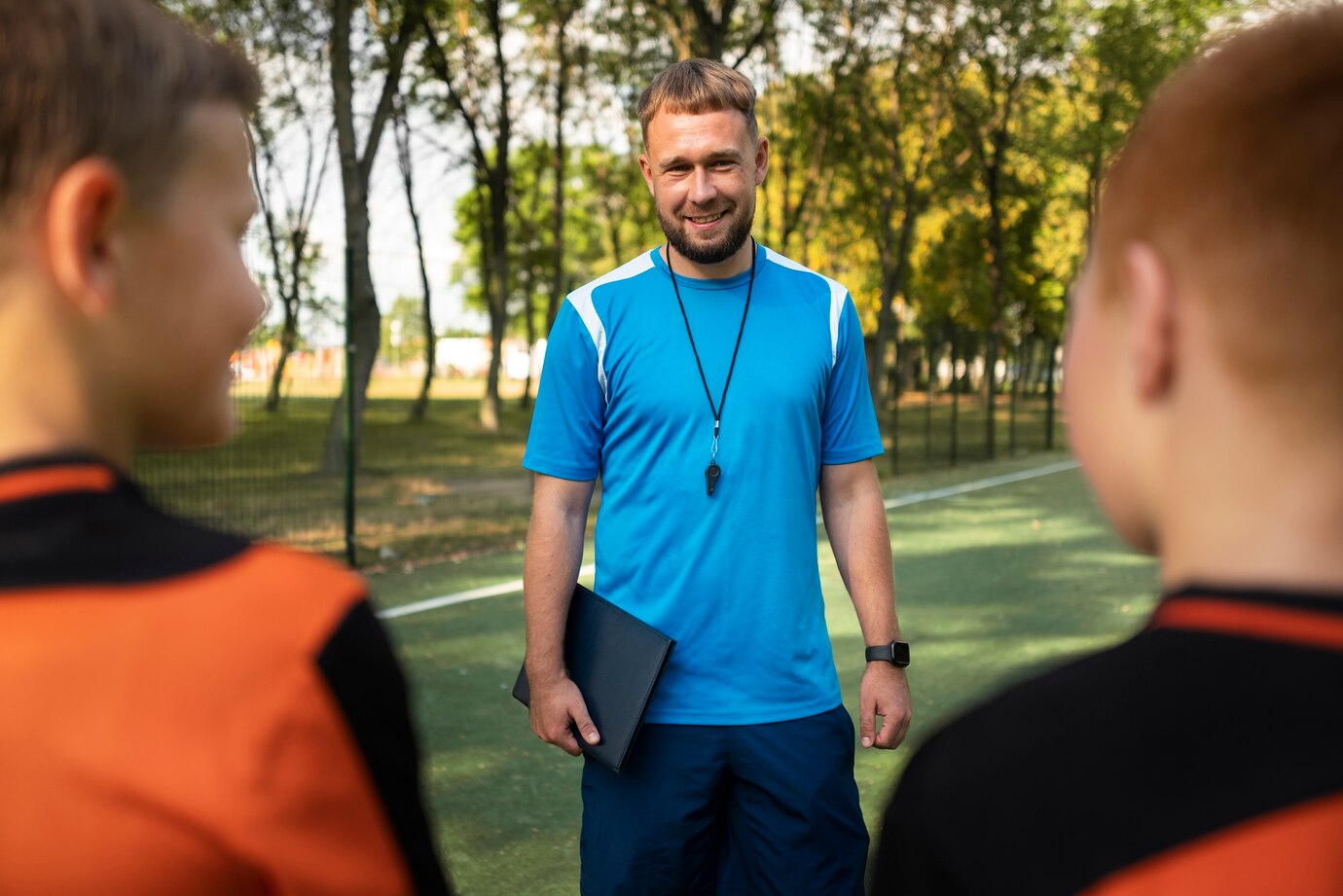
Life After Stroke: Regaining Independence with Transportation, Social Activities & Work (Community Reintegration)
Share IT

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.
Categories
Community Reintegration After Stroke
Rebuilding a Life Following a Stroke: Transportation, Social Activities, and Vocational Rehabilitation for Community Reintegration
Stroke interrupts lives and frequently leaves survivors with mental and physical problems that interfere with day-to-day functioning. Regaining physical function and abilities is the main goal of rehabilitation, but the vital next stage is community reintegration, which is going back to leading an independent and satisfying life in the community. Three essential components of a successful community reintegration are examined in this blog post: transportation, social activities, and vocational rehabilitation.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!Table of Contents
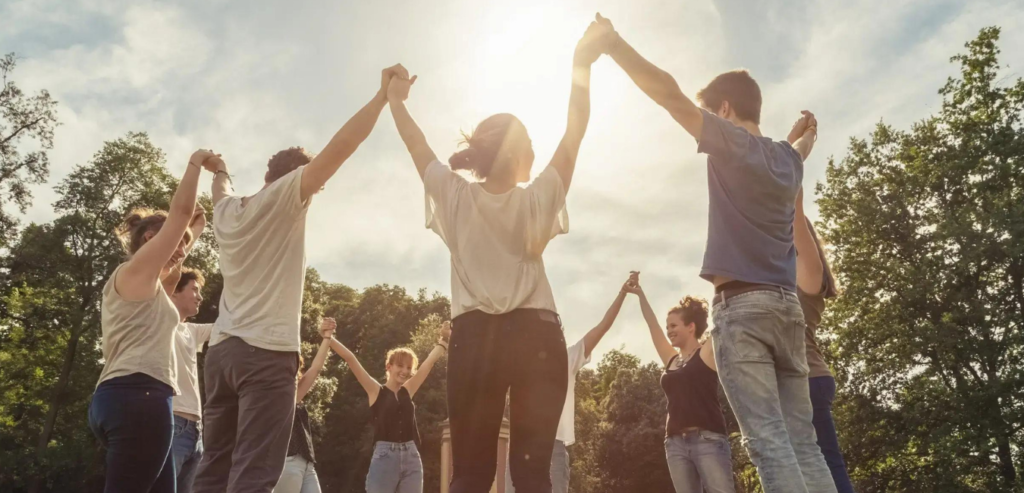

Why Is Reintegration Into the Community Important?
Community Reintegration After Stroke
Reintegrating into the community has many advantages for stroke survivors:
- Better mental and physical health: Engaging in social activities and making new connections with loved ones helps people feel less alone and more purposeful by rekindling their sense of purpose.
- Enhanced independence: Being able to use transit on one’s own again gives one a feeling of freedom and control.
- Improved self-esteem: Going back to work or taking part in worthwhile activities might help you feel more confident and valuable.
- Enhanced general quality of life: Through community reintegration, stroke victims can fully engage in life and give back to their communities.
Community Reintegration’s Obstacles
Community Reintegration After Stroke
After a stroke, a number of variables may make community reintegration difficult:
- Physical restrictions: Difficulties utilizing public transportation or mobility impairments could be problematic.
- Cognitive impairments: Planning and engaging in tasks may be difficult due to memory issues or organizational issues.
- Fatigue: The weariness that follows a stroke might restrict one’s energy and social engagement.
- transit barriers: Difficulties driving safely or a lack of accessible transit may limit mobility.
- Fear of social interaction: Social disengagement may result from anxiety related to social situations or worries about cognitive limits.
Overcoming Obstacles and Strategies for Reintegration
Community Reintegration After Stroke
Transport:
- Investigating accessible transportation options: Paratransit services, ride-sharing applications with accessible features, and public transportation with ramps and allocated seating can all assist in navigating transportation demands.
- Driver rehabilitation: Occupational therapists can evaluate a person’s driving abilities and suggest modifications or training courses if they want to start driving again.
- Community transportation services: Senior transportation programs and accessible transportation for those with disabilities are provided by several municipalities.
Social Engagement:
- Support groups: Stroke support groups offer a forum for sharing experiences and interacting with others going through comparable difficulties.
- Social interests and hobbies: Regaining social connections and a sense of normalcy might be facilitated by partaking in interests or hobbies from before the stroke.
- Volunteering: Giving back to causes that are important to you can provide a sense of purpose and social contact.
Community centers, often known as senior centers, frequently provide chances for social interaction, fitness programs, and get-togethers.
Rehabilitation of the Vocational Field:
Community Reintegration After Stroke
- Vocational assessment: Evaluating abilities and limits enables one to ascertain whether going back to work is possible and what adjustments might be required.
- Retraining or job training: Programs can assist people in learning new skills or retraining for positions that better fit their present skill set.
- Workplace adjustments: Companies may be able to meet employees’ demands by making scheduling adjustments, providing flexible work arrangements, or making equipment adjustments.
The Function of Friends, Family, and Medical Professionals
Community Reintegration After Stroke
A team effort is necessary for successful community reintegration. In addition to offering emotional support and, if possible, transportation assistance, family and friends can encourage social engagement. Therapists, social workers, and vocational rehabilitation specialists are examples of healthcare professionals who can be extremely important in:
- recognizing the obstacles to reintegration.
- creating a customized plan for reintegration into the community.
- putting stroke victims in touch with pertinent resources and assistance programs.
In conclusion, an empowerment journey
Community Reintegration After Stroke
Reintegrating back into the community after a stroke is an ongoing process that need for persistence and assistance. Stroke survivors can reconstruct their life, reclaim their independence, and reintegrate into their communities by confronting transportation issues, participating in social events, and investigating career opportunities. Recall that stroke survivors can create the conditions for a happy and meaningful life after stroke by dedicating themselves to self-advocacy and building a network of support.

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.






















































Recent Comments