Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Understanding Symptoms, Causes, and Prevention
Share IT

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.
Categories
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Cardiovascular Disease (CAD): The Silent Danger to Your Heart
The illness known as coronary artery disease (CAD) is characterised by the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries, which feed blood to the heart. Plaque, or the accumulation of fat on the inner walls of the arteries, is the main cause of this narrowing. Although CAD frequently advances gradually for years, its effects can be fatal. In-depth information about CAD’s causes, symptoms, risks, and prevention strategies are provided in this blog post.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!Table of Contents
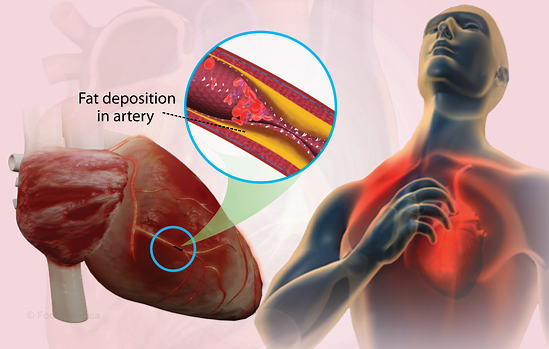
The Principal Actors: Your Arteries Coronarios and Arteries Plaque Arteriarios:
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
- Coronary Arteries: The blood that is rich in oxygen is transported from your heart to the heart muscle by these essential blood arteries. Unhindered blood flow is ensured by elastic, smooth coronary arteries.
- Plaque: This complicated accumulation of cholesterol, fats, cellular waste materials, calcium, and fibrin (a clotting element) within the coronary arteries. Plaque narrows and hardens the arteries over time, preventing blood flow to the heart muscle.
The Man Behind the Curtain: Coronary Artery Disease Causes
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
The following elements are involved in the development of CAD:
- Atherosclerosis: As previously indicated, the main cause of CAD is plaque accumulation brought on by atherosclerosis.
- High Cholesterol: High LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels are a primary contributing factor to high cholesterol. Plaque can develop as a result of LDL cholesterol building up in the artery walls.
- High Blood Pressure: Prolonged high blood pressure accelerates the formation of plaque by weakening and damaging the artery walls.
- Smoking: Smoking causes blood clotting, inflammation, and damage to the artery lining, all of which are factors in the development of CAD.
- Diabetes: This illness can cause elevated blood sugar levels, which can damage blood vessels and increase inflammation. These two factors can hasten the development of CAD.
- Family History: Your risk is increased if you have a close relative who has CAD.
- Unhealthy Diet: Consuming a lot of processed foods, added sugar, and saturated and trans fats can raise inflammation and aggravate cholesterol.
- Physical Inactivity: Insufficient exercise raises the risk of cardiovascular disease and raises harmful cholesterol levels.
The Quiet Robber at Work: Signs and Consequences of CAD
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
A common feature of CAD is that it generally advances with little to no symptoms until the arterial narrowing gets severe enough to severely limit blood flow. This may result in:
- Angina, or chest pain: can happen when plaque accumulation restricts blood flow to the heart muscle. This is particularly common during physical activity or stressful situations emotionally.
- Heart Attack: A heart attack is a potentially fatal condition in which the heart tissue is completely starved of oxygen and nutrients due to a blood clot blocking a coronary artery.
- Heart Failure: Prolonged CAD can weaken the heart’s muscle, which makes it harder for the heart to pump blood efficiently and ultimately results in heart failure.
Retaliating: Techniques for Avoiding and Handling CAD
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
The good news is that leading a heart-healthy lifestyle can dramatically lower your chance of developing CAD and associated complications:Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
- A healthy diet: should be limited in processed foods, added sugar, and saturated and trans fats. Give ample attention to whole grains, fruits, veggies, and lean protein sources.
- Regular activity: Try to get in at least 150 minutes a week of moderate-to-intense activity or 75 minutes a week of vigorous exercise. Any kind of exercise is preferable to none at all.
- Weight control: Keeping your weight within a healthy range eases the strain on your heart and blood vessels.
- Cessation of Smoking: One of the most effective things you can do to avoid CAD and enhance your general health is to give up smoking.
- Manage Blood Pressure and Cholesterol: Consult your physician to modify your lifestyle and, if necessary, take medication to control your blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- Control Diabetes: In order to avoid complications like CAD, it’s imperative that you keep an eye on your blood sugar levels if you have diabetes.
- Medication: Depending on your specific needs, your doctor may recommend drugs to control blood pressure, cholesterol, and stop blood clots.
Conclusion: Preserving the Health of Your Heart
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Although coronary artery disease is a dangerous condition, you can greatly lower your risk by making heart-healthy living a priority and collaborating closely with your physician to control risk factors. The prevention of consequences such as heart attack and heart failure is largely dependent on early detection and treatment. Recall that managing your heart health now can guarantee a better and more prosperous tomorrow.

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.






















































Recent Comments