Diabetes & Stroke Risk: Double Trouble and How to Manage It
Share IT

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.
Categories
Diabetes and Stroke Prevention
Knowing the Connection Between Diabetes and Stroke Risk in Double Jeopardy
A stroke damages brain cells by obstructing blood flow to the brain, which is one of the main causes of mortality and disability worldwide. A chronic disease called diabetes mellitus that affects blood sugar regulation greatly raises the risk of stroke. This blog post explains the intricate relationship between diabetes and stroke, giving you the knowledge and confidence to take charge of your health now and in the future.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!Table of Contents
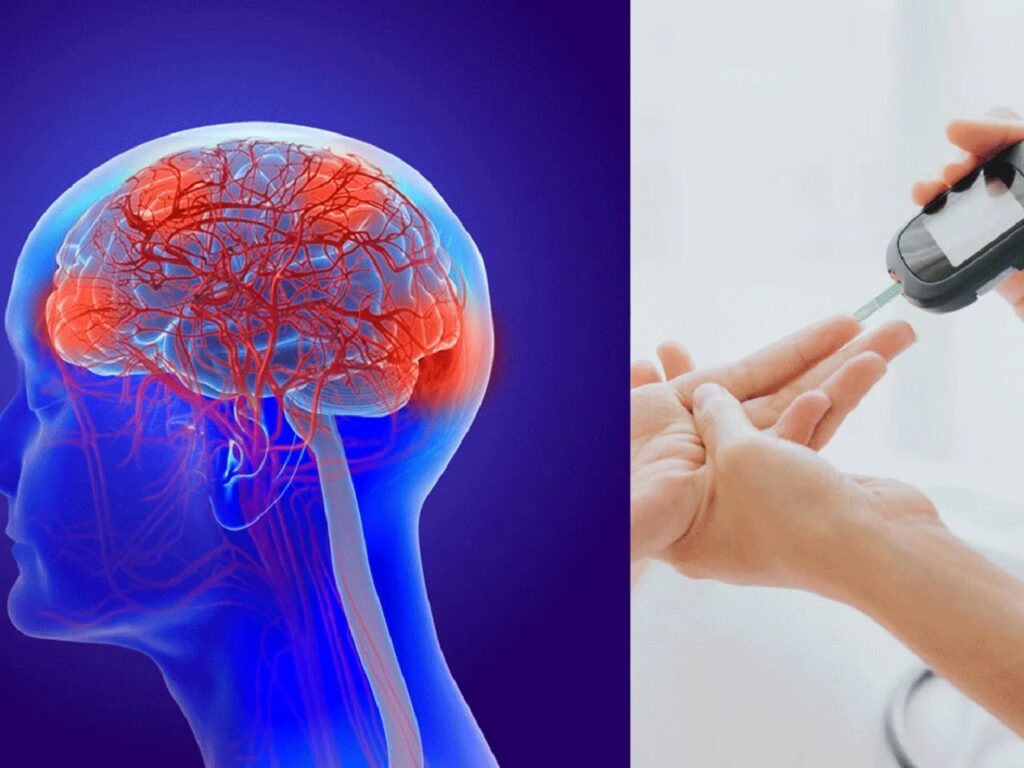
Diabetes Mellitus: What Is It?
Diabetes and Stroke Prevention
Diabetes, often known as diabetes mellitus, is a long-term medical illness marked by elevated blood sugar levels. Insulin is a hormone that controls blood sugar; either your body produces too little of it or your cells develop resistance to its effects. This causes the blood to become too sugared, which can cause a number of health issues.
Diabetes Types and Stroke Risk:
Diabetes and Stroke Prevention
- Type 1 Diabetes: In type 1 diabetes, there is minimal or no insulin production by the body. Despite being less prevalent, those with type 1 diabetes have a higher risk of stroke than the overall population.
- Type 2 diabetes: The most common type of diabetes, known as type 2, is characterised by insufficient insulin production or increased insulin resistance in the body. The risk of stroke is much higher in those with type 2 diabetes than in people without the disease.
How Stroke Risk Is Raised by Diabetes:
Diabetes and Stroke Prevention
Diabetes increases the risk of stroke through a number of mechanisms:
- Damaged Blood Vessels: The inner lining of blood vessels is harmed by persistently high blood sugar levels, which increases their susceptibility to inflammation and hardness (atherosclerosis). The risk of stroke can rise due to decreased blood supply to the brain caused by this artery narrowing.
- High Blood Pressure: High blood pressure is a major risk factor for stroke and frequently coexists with diabetes. Elevated blood pressure worsens blood vessel damage and raises the possibility of a stroke.
- Increased Risk of Blood Clotting: Diabetes can change the body’s clotting processes, which raises the possibility of blood clots accumulating in arterial walls. A stroke can result from these clots travelling to the brain and obstructing blood flow.
- Enhanced Inflammation: Diabetes-related chronic inflammation raises the risk of stroke and damages blood vessels.
Controlling Diabetes and Lowering the Risk of Stroke:
Diabetes and Stroke Prevention
The good news is that you can lower your risk of stroke greatly by effectively controlling your diabetes. How to do it is as follows:
- Maintain Healthy Blood Sugar Levels: Create a customised strategy with your doctor to control your blood sugar levels using food, exercise, and medication if necessary.
- Control Blood Pressure: Reducing the risk of stroke requires routine blood pressure monitoring and management. It can be required to take medication or make lifestyle adjustments to maintain appropriate blood pressure levels.
- Sustain a Healthy Weight: Reducing body fat and keeping a healthy body mass index (BMI) will help manage blood sugar levels and lower the risk of stroke.
- Consume a Healthful Diet: Select a well-balanced diet that is low in processed foods, added sugars, trans fats, and saturated fats. Choose lean protein sources, healthy grains, fruits, and veggies.
- Exercise Frequently: Regular exercise lowers the risk of stroke by lowering inflammation, enhancing blood flow, and controlling blood sugar levels.
- Give Up Smoking: Smoking greatly raises the risk of stroke in people with diabetes. Giving up smoking is one of the best things you can do for your health.
- Handle Stress: Prolonged stress can make blood sugar regulation more difficult. To reduce stress, engage in stress-reduction exercises like yoga or meditation.
The Key is Early Detection and Treatment:
Diabetes and Stroke Prevention
It is essential to diagnose and treat diabetes early in order to avoid complications such as stroke. Talk to your doctor about diabetes screening if you have any risk factors or a family history of the disease. You can greatly reduce your risk of stroke and other complications associated to diabetes by implementing early intervention.
In summary:
Diabetes and Stroke Prevention
The risk of stroke is markedly increased by diabetes mellitus. However, you can lower your risk of stroke greatly with good diabetes treatment, a healthy lifestyle, and frequent check-ups. Discuss your risk of stroke with your physician and work out a customised plan to control your diabetes and safeguard your mental well-being.

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.






















































Recent Comments