Heart Diagnostic Tests
Revealing the Heart’s Condition: An Overview of Diagnostic Procedures
The heart is a life-giving organ that should be treated with the greatest care. To keep your heart healthy, it’s important to find any underlying problems early. Thankfully, there are several diagnostic procedures available to assess heart health and pinpoint possible issues. This blog post explores the five main tests—coronary angiography, stress testing, echocardiograms, cardiac catheterization, and electrocardiogram/ECG/EKG—that are used to diagnose heart illness.
Table of Contents
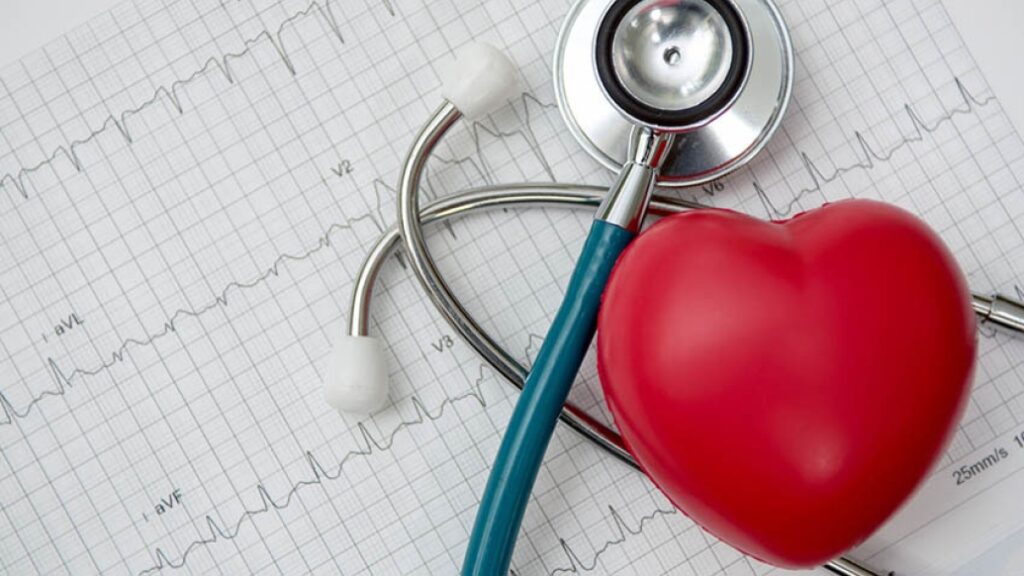
- Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG): A Momentary Record of the Electrical Activity of the Heart
The most popular non-invasive test for determining the electrical activity of the heart is an ECG. Your arms, legs, and chest are fitted with tiny electrodes that capture the electrical signals produced by your heartbeat. The printout that results is a trace with peaks and waves that provides details about:Heart Diagnostic Tests
- Heart rhythm: An erratic heartbeat may be a sign of arrhythmias, whereas a regular beating suggests that the heart is healthy.
- Heart rate: The test determines whether your heart rate is excessively fast (tachycardia) or too slow (bradycardia).
- Damage to the heart muscle: Deviant patterns on the tracing may point to current or previous heart muscle damage.
Heart Diagnostic Tests
The ECG is a rapid, painless test that usually takes five to ten minutes. It can be used to track heart health over time and is a useful tool for initial screening.
- Stress Test: Applying Pressure on the Heart
A stress test assesses the heart’s reaction to physical strain. It combines blood pressure and occasionally oxygen level monitoring with an ECG. There are mostly two kinds:Heart Diagnostic Tests
- Exercise stress test: You use a treadmill to walk or run more and harder while having your heart rate tracked. This mimics how the heart would react to activity and aids in locating any restrictions on blood supply to the heart muscle.
- Pharmacological stress test: In the event that physical activity is not feasible, intravenous drugs that replicate the effects of physical activity are used to raise blood pressure and heart rate.
Heart Diagnostic Tests
The stress test aids in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease (CAD), a condition in which the heart’s blood vessels narrow due to plaque accumulation. The exam may identify symptoms such as angina, or chest pain that occurs during physical effort.
- Echocardiogram: Revealing the Structure and Operation of the Heart
An echocardiogram, also referred to as an echo, is a type of ultrasound imaging procedure that produces a live video image of your heart. Sound waves are employed to evaluate:
- Size and shape of the heart: An enlarged or abnormally shaped heart may be a sign of underlying cardiac issues.
- Heart valve function: A good functional heart valve ensures adequate blood flow through the heart, which the echo can detect.
- Heart wall movement: The test evaluates the heart’s pumping efficiency by measuring how well the heart muscle contracts and relaxes with each beat.
- Heart blood flow: Deviations from normal heart chamber blood flow patterns can be identified using echocardiography.
An echo can be done in a number of ways and is a painless procedure:
- Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE): A probe is used to drive sound waves through the chest wall.
- Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE): To get a better look at the heart, a tiny probe is sent into the esophagus.
Heart Diagnostic Tests
The echo helps diagnose a number of heart disorders, including as heart failure, valve issues, and congenital cardiac anomalies, by providing comprehensive information on the anatomy and function of the heart.
- Heart Catheterization: An Up-close View of the Heart
Direct visualization of the coronary arteries is possible for medical professionals through a minimally invasive procedure called cardiac catheterization, or cardiac cath. A tiny, flexible tube called a catheter is sent through the blood arteries and into the heart by being put into an artery in the wrist, arm, or groin.
In the process:
Heart Diagnostic Tests
- Coronary angiography: To identify any blockages in the coronary arteries, a contrast dye is administered via the catheter and X-ray images are obtained.
- Additional steps: Further treatments such as balloon angioplasty (to open restricted arteries) or stent insertion (to maintain arteries open) may be carried out during the same catheterization, depending on the results.
Heart Diagnostic Tests
Compared to the tests listed above, cardiac catheterization is a more involved operation that is usually used to identify complex heart diseases or in response to aberrant ECG, stress test, or echo results.
- Coronary Angiography: Exposing Coronary Artery Blockages
Frequently carried out in conjunction with a cardiac catheterization, coronary angiography makes use of X-ray imaging to view the coronary arteries and identify blockages brought on by plaque accumulation. The coronary arteries are made visible in the X-ray pictures by injecting a contrast dye into them. This enables medical professionals to:

![Heart Disease in Children & Teens: Beyond Birth Defects [Symptoms, Types & Treatment] 2 Heart Disease in Children](https://ktechkhalil.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/OIP-3-110x110.jpg)
