Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Recognize the Signs of Brain Bleed
Share IT

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.
Categories
Intracerebral Hemorrhage Symptoms and Treatment
Understanding Brain Bleeding Intracerebralbleeding
Strokes can be roughly classified into two primary types: ischemic (blood flow obstruction) and hemorrhagic (brain bleeding). Strokes are a leading cause of disability and death globally. The most prevalent kind of hemorrhagic stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), is the subject of this blog post. In ICH, a weak blood artery bursts inside the brain tissue, accumulating blood and applying pressure to nearby brain cells. This may result in numerous crippling symptoms as well as serious brain damage.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!Table of Contents
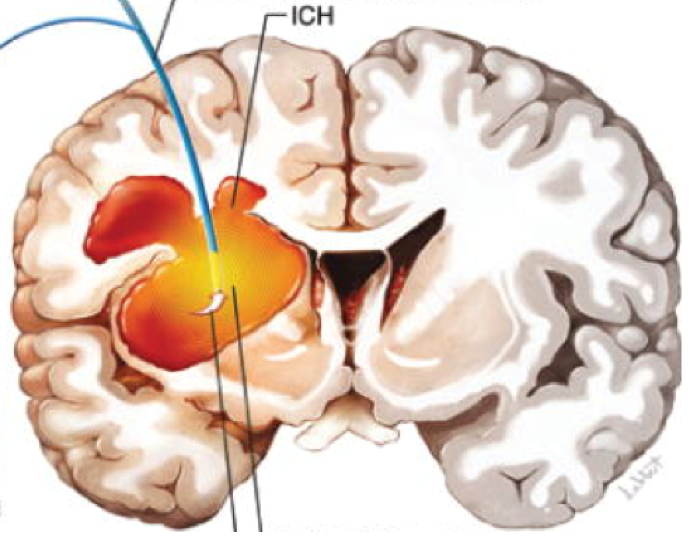
An Internal Vessel Broken: The Mechanism of Intracerebral Hemorrhage
The brain depends on blood arteries to provide it with an ongoing supply of nutrients and oxygen. When an intracerebral hemorrhage occurs, blood seeps into the surrounding brain matter via the rupture of a weak blood artery within the brain tissue. ICH comes in two primary subtypes:
- Primary ICH: The most prevalent kind of ICH, known as primary ICH, is frequently brought on by unchecked hypertension. The walls of blood vessels become weaker with prolonged high blood pressure, increasing the risk of rupture.
- Secondary ICH: There are a number of reasons why this kind of bleeding might happen, such as:
Intracerebral Hemorrhage Symptoms and Treatment
- Usage of drugs that thin the blood
- rupture of an aneurysm, a weak spot in the wall of a blood vessel
- An aberrant link between arteries and veins is known as an arteriovenous malformation (AVM).
- Head injuries
- Brain tumors
Intracerebral Hemorrhage Risk Factors: Who Is Most at Risk?
Intracerebral Hemorrhage Symptoms and Treatment
The following variables raise your chance of having an intracerebral hemorrhage:
- High blood pressure: The main risk factor for primary ICH is uncontrolled hypertension.
- Age: As people age, their risk of ICH rises.
- Atherosclerosis: The accumulation of plaque in blood vessel walls can deteriorate them and raise the possibility of a rupture.
- Amyloid angiopathy: is a disorder in which the walls of blood vessels become more liable to burst due to an accumulation of the protein amyloid.
- Blood thinners: Drugs intended to stop blood clots can make bleeding—including intracerebral hemorrhage—more likely.
- Heavy drinking: Drinking too much alcohol can harm blood vessels and raise blood pressure.
- Smoking: Smoking raises the risk of high blood pressure and destroys blood vessels.
- Use of cocaine: Using cocaine can result in an abrupt increase in blood pressure, which can lead to ICH.
Intracerebral Hemorrhage Warning Signs: Identifying the Risk
Intracerebral Hemorrhage Symptoms and Treatment
Intracerebral hemorrhage symptoms can be fairly severe and develop suddenly. Here are some things to be aware of:
- An abrupt and intense headache: Often referred to as a “thunderclap” headache, this is the worst headache you have ever experienced.
- Nausea and vomiting: The intense headache may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
- Seizure activity: During an ICH, some people have seizures.
- Consciousness loss: The degree of bleeding may cause a person to lose consciousness.
- One side of the body weakness or paralysis: This might impair arm or leg movement.
- Vision issues: One or both eyes may experience sudden double vision or blurriness.
- Speech slurring or difficulty understanding: Speech may get hard to understand or pronounce.
Intracerebral Hemorrhage Symptoms and Treatment
Move Quickly: Get medical help right away if you encounter any of these symptoms. Improving results and reducing brain damage require early identification and treatment.
Finding the Source of an Intracerebral Hemorrhag
Starting Treatment Early detection is crucial to stopping more bleeding. Usually, medical professionals use a mix of tests:
- Physical examination: Your reflexes, muscle strength, coordination, and speech will all be evaluated during a neurological exam.
- Brain imaging tests: Because CT scans may identify blood in the brain, they are the test of choice for detecting ICH. MRI could be utilized for additional assessment.
- Angiography: This imaging modality shows how blood flows through the arteries in order to spot possible AVMs or aneurysms.
Intracerebral Hemorrhage Symptoms and Treatment
Doctors can adjust treatment by determining the source and location of the bleeding.
Strategies for Treating Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Ceasing the Bleeding and Safeguarding the Brain
Intracerebral Hemorrhage Symptoms and Treatment
Controlling bleeding, lowering brain pressure, and avoiding complications are the main objectives of managing intracerebral hemorrhage. The primary therapeutic modalities are as follows:
- Medication: Blood pressure drugs are used to lower blood pressure and manage bleeding.
- Surgery: To stop further bleeding, it may occasionally be required to remove an AVM or clip an aneurysm.
- Minimally invasive procedures: To stop bleeding blood arteries, endovascular embolization is one technique that can be performed.
- Supportive care: Drugs can be used to reduce swelling, control pain, and stop seizures.
Intracerebral Hemorrhage Symptoms and Treatment
The precise course of treatment will be determined by the extent of the bleeding, where the bleeding is occurring, and your general

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.






















































Recent Comments