Breathe Easier with COPD: A Guide to Long-Term Oxygen Therapy (LTOT)
Share IT

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.
Categories
Long-Term Oxygen Therapy for COPD
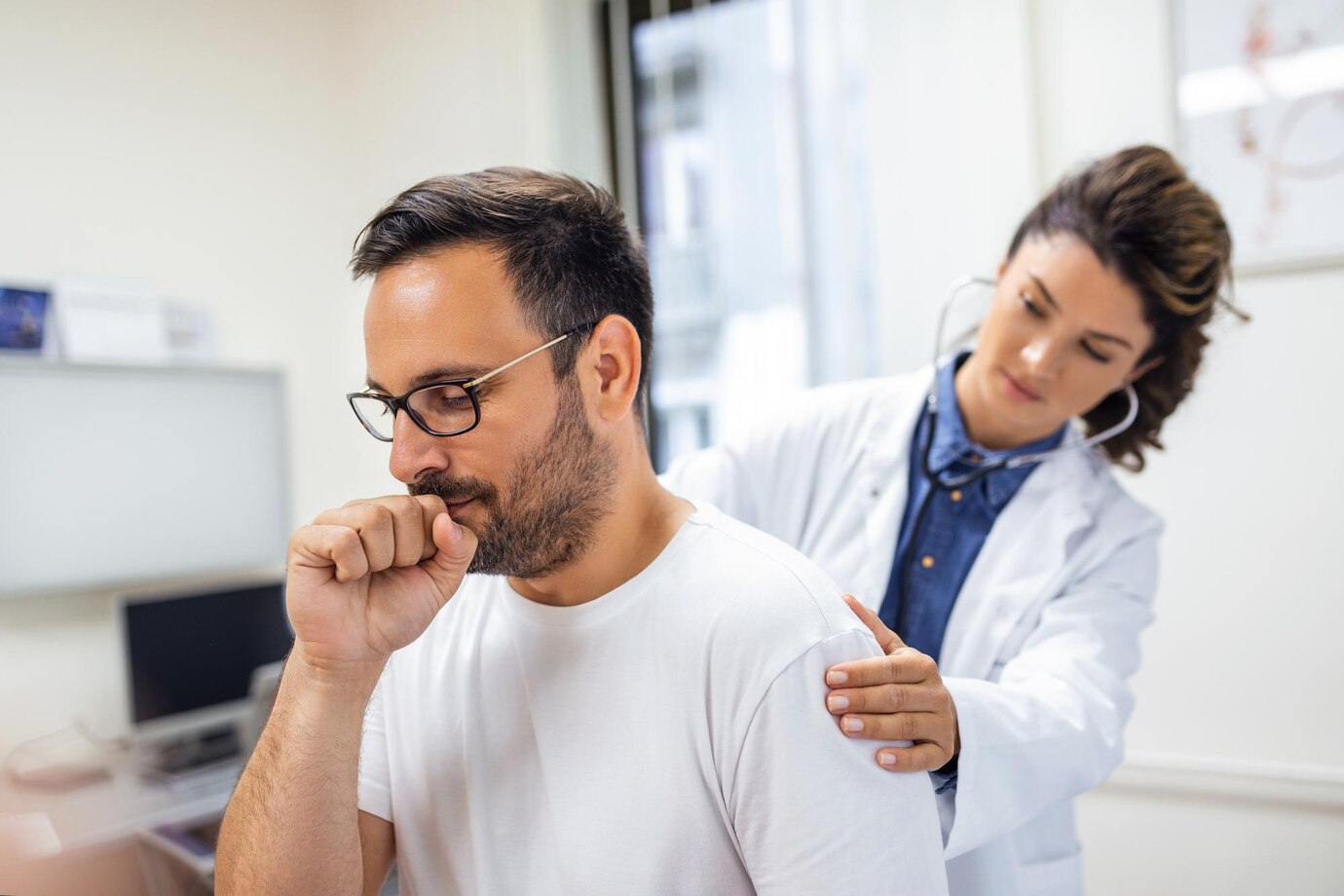
Breathe a sigh of relief: Chronic hypoxemia with long-term oxygen therapy (LTOT) for COPD
Airflow restriction is a hallmark of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), a progressive lung illness. Some COPD patients experience persistent hypoxemia, a disease in which the blood oxygen level falls below a safe level, as their illness worsens. Under such circumstances, long-term oxygen therapy (LTOT) emerges as a critical intervention for the management of COPD and the enhancement of life quality. In-depth discussions of LTOT’s advantages, uses, modes of administration, and pragmatic issues for COPD patients with persistent hypoxemia are provided in this article.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!Table of Contents
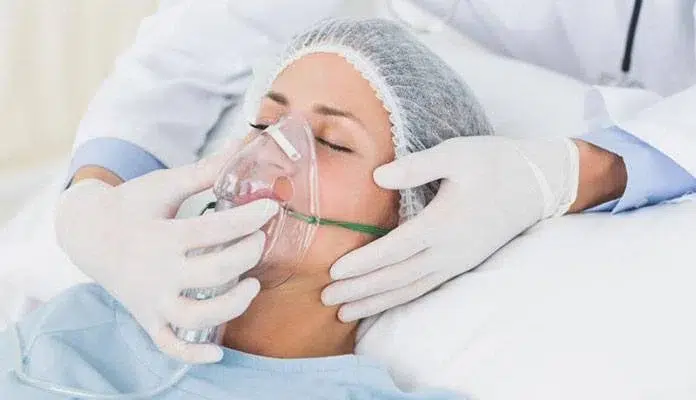
Recognizing COPD-Related Chronic Hypoxemia
Long-Term Oxygen Therapy for COPD
Well-functioning lungs effectively draw oxygen from the surrounding air and deliver it to the blood. This process is hampered in COPD by weakening lung tissue and damaged airways. Hypoxemia, a condition where blood oxygen levels fall, is the result of this. Low oxygen levels that are persistent, or chronic hypoxemia, can lead to a number of problems, such as:
Long-Term Oxygen Therapy for COPD
- Breathlessness is a classic sign of COPD that gets worse with hypoxemia.
- Fatigue: Reduced oxygen flow to tissues can make you feel more exhausted and less able to exert yourself.
- Cognitive impairment: Memory, attention, and attentiveness can all be negatively impacted by a prolonged oxygen shortage in the brain.
- Increased risk of complications: Heart issues and pulmonary hypertension, or elevated blood pressure in the lungs, can be brought on by hypoxemia.
LTOT’s Function in the Management of COPD
Long-Term Oxygen Therapy for COPD
In LTOT, patients with persistent hypoxemia receive supplemental oxygen either continuously or almost continuously to increase blood oxygen levels and alleviate symptoms. While LTOT cannot reverse the effects of COPD, it is an essential tool for managing its symptoms and enhancing quality of life.
Advantages of long-term care:
- Diminished Symptoms: LTOT efficiently reduces exhaustion, dyspnea, and enhances the quality of sleep.
- Enhanced Activity Levels: Patients can lead more active lives and engage in everyday activities more easily with better oxygenation.
- Enhanced Cognitive Function: Memory, mental clarity, and cognitive function are all enhanced by adequate oxygen flow.
- Decreased Hospitalizations: LTOT may help avoid hypoxemia-related problems, which may lower the need for hospital admissions.
For whom does LTOT apply?
Long-Term Oxygen Therapy for COPD
Not every patient with COPD needs LTOT. Your blood oxygen levels as determined by arterial blood gas (ABG) testing will be used by your doctor to assess your eligibility. LTOT is typically diagnosed when your resting oxygen saturation drops below a certain threshold (typically less than 88 mmHg) or when you experience hypoxemia throughout the daytime and exhibit certain symptoms like edema (ankle swelling) or cor pulmonale (right-sided heart failure from COPD).
Delivery Networks for Long-Term Operations
Long-Term Oxygen Therapy for COPD
For LTOT, there are multiple methods of supplemental oxygen delivery. Your physician will advise you on the best system based on your needs and way of life.
- Stationary Concentrators: These electrical machines provide concentrated oxygen by using the surrounding air. They offer a steady supply of oxygen and are usually used at home.
- Systems for storing liquid oxygen: which vaporizes to produce breathable gas, are known as liquid oxygen systems. They need to be refilled but provide some portability.
- Compressed oxygen cylinders: Compressed oxygen gas is stored in these transportable tanks. Despite being portable, they have a finite amount of oxygen and need to be filled frequently.
Practical Tips for Users of LTOT
Long-Term Oxygen Therapy for COPD
Although there are some modifications needed, living with LTOT has several advantages. Here are some important things to think about:
- Maintaining Consistency Is Essential: To get the most out of LTOT, it must be used correctly and consistently.
- Options for Portability: When going on an excursion, portable concentrators allow for greater movement while continuing oxygen therapy.
- Travel-Related Considerations: Consult your physician about your travel schedule to guarantee that you receive oxygen on the fly.
- Safety precautions: Oxygen burns quite easily. Keep oxygen away from cigarettes, open flames, and heat sources, and practice fire safety.
- Continual Upkeep: To guarantee optimal performance, adhere to your doctor’s instructions for routine maintenance of your oxygen equipment.
Getting by with LTOT
Long-Term Oxygen Therapy for COPD
For the management of COPD with chronic hypoxemia, LTOT is an effective technique. Working with your physician, selecting the best delivery method, and adhering to safety procedures can all help you live a far better life. Recall that LTOT gives you the freedom to live a richer life with COPD and to breathe easier. It does not limit you.

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.






















































Recent Comments