RNA Splicing Drugs: New Study Unlocks Secrets for Better Treatments
Share IT

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.
Categories
RNA Splicing Drugs
RNA Splicing Drugs: A Novel Study Provides Light on Drug Design
The medical industry is always changing as scientists delve deeper into the complex processes of human cells to create more specialised and potent medicines. The mechanism of action of RNA splicing medications has been clarified by a recent ground-breaking study, providing important information for the development of more effective treatments.
Comprehending RNA Splicing: The Guidelines Incorporated
RNA Splicing Drugs
While our DNA contains the genetic information that makes us who we are, messenger RNA (mRNA) is the molecule that contains the instructions needed to make proteins, which are the workhorses of our cells. mRNA isn’t a direct replica of DNA, though. It goes through a procedure known as RNA splicing, in which some bits are cut off and the remaining pieces are sewn together. The final protein product is determined by this splicing process.
Table of Contents
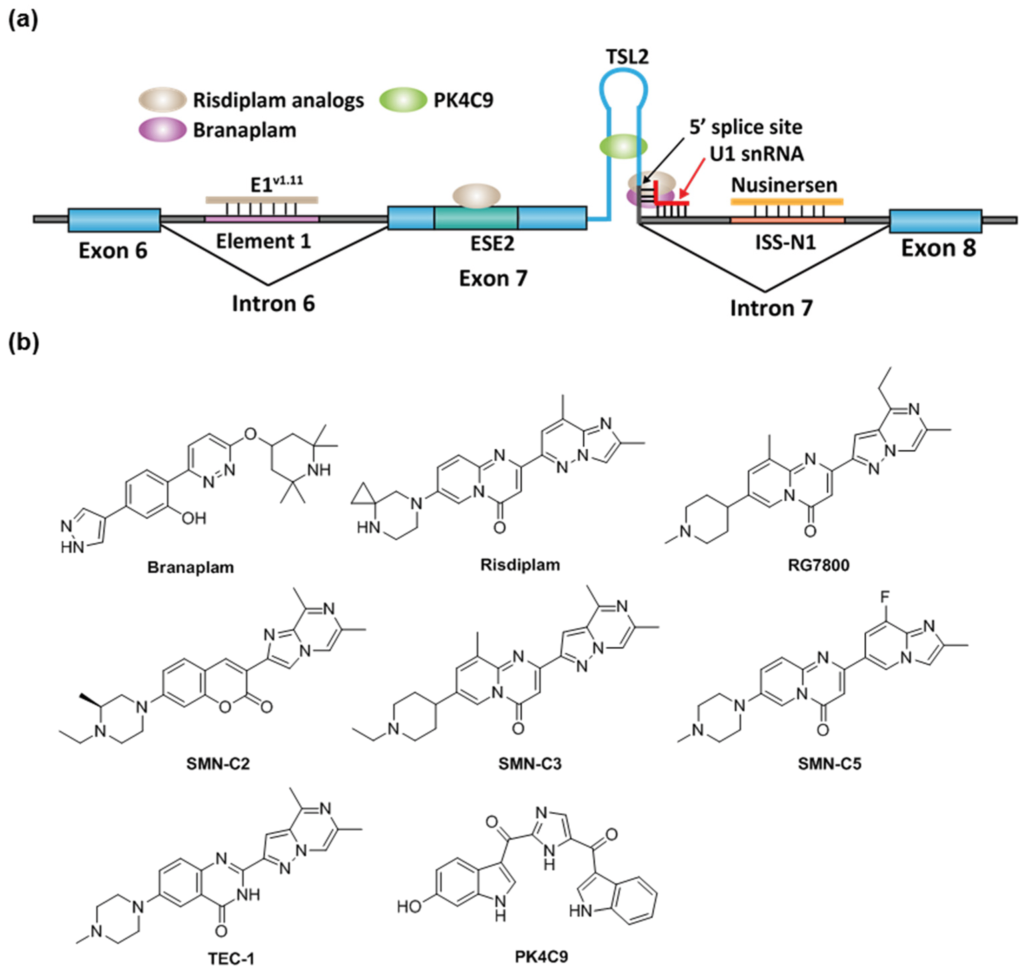
Targeting Splicing: A Hopeful Treatment Strategy
RNA Splicing Drugs
Mistakes in the synthesis of proteins give birth to numerous illnesses. This could occur if aberrant proteins are produced as a result of improper RNA splicing. This is the role of RNA splicing medications. These medications work by modifying the splicing process to fix mistakes and guarantee the synthesis of healthy proteins.
It has proven difficult to create RNA splicing medications that are both targeted and efficacious. Until recently, scientists were unsure of how these medications interacted with the intricate machinery that is involved in RNA splicing.
The New Research: Revealing the Enigma
RNA Splicing Drugs
The goal of this ground-breaking study was to understand how RNA splicing medications work. Sophisticated tools were utilised by researchers to watch how the medications bind to particular RNA molecules and affect splicing activities. Their research provided important information about:
- Medication-RNA Interactions: The research pinpointed the exact sites on the RNA molecule where the medications attach. This information is essential for creating medications with increased specificity and affinity while reducing side effects.
- Engagement of Splicing Machinery: The study elucidated the manner in which the medications engage with the cellular apparatus accountable for splicing. With this knowledge, scientists may precisely control the splicing process by customising medications that affect particular steps in the process.
- Cellular Context: The investigation looked at how the medications’ efficacy is affected by the cellular milieu. This information is essential for creating medications that work well in the intricate biological environment of a cell.
Consequences for More Effective Therapy
RNA Splicing Drugs
The results of this study mark a substantial advancement in the creation of medications that splice RNA. Now that scientists know how these medications function at the molecular level, they can:
- Develop More Targeted medications: By developing more targeted medications that minimise off-target effects, researchers can more precisely target certain RNA sequences with a better understanding of drug-RNA interactions.
- Enhance Medication Administration: Through comprehending the function of the cellular milieu, researchers can devise tactics to administer medications to their intended RNA molecules within cells with greater efficiency.
- Extend Your Options for Treatment: The creation of RNA splicing medications to treat a greater variety of disorders brought on by splicing faults is made possible by this research.
The Prospects for RNA Splicing Treatments
RNA Splicing Drugs
A significant advancement in the field of RNA splicing therapy has been made by this study. Researchers are now better able to create more focused and efficient treatments for a variety of disorders because the mechanism of action of these medications has been made more clear. A new class of RNA splicing medications is predicted to develop as research advances, providing patients with illnesses for which conventional treatments are insufficient hope.

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.






















































Recent Comments