Wyoming Mule Deer Face CWD Threat: A Race Against Time
Share IT

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.
Categories
Wyoming Mule Deer and CWD
Shadow Across the Sagebrush: The Danger of CWD for Wyoming Mule Deer
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!In Wyoming, there is a serious threat to the magnificent mule deer, which is considered an emblem of the American West. Some herds are being devastated by Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD), a prion disease related to mad cow disease that is driving them to the verge of extinction.
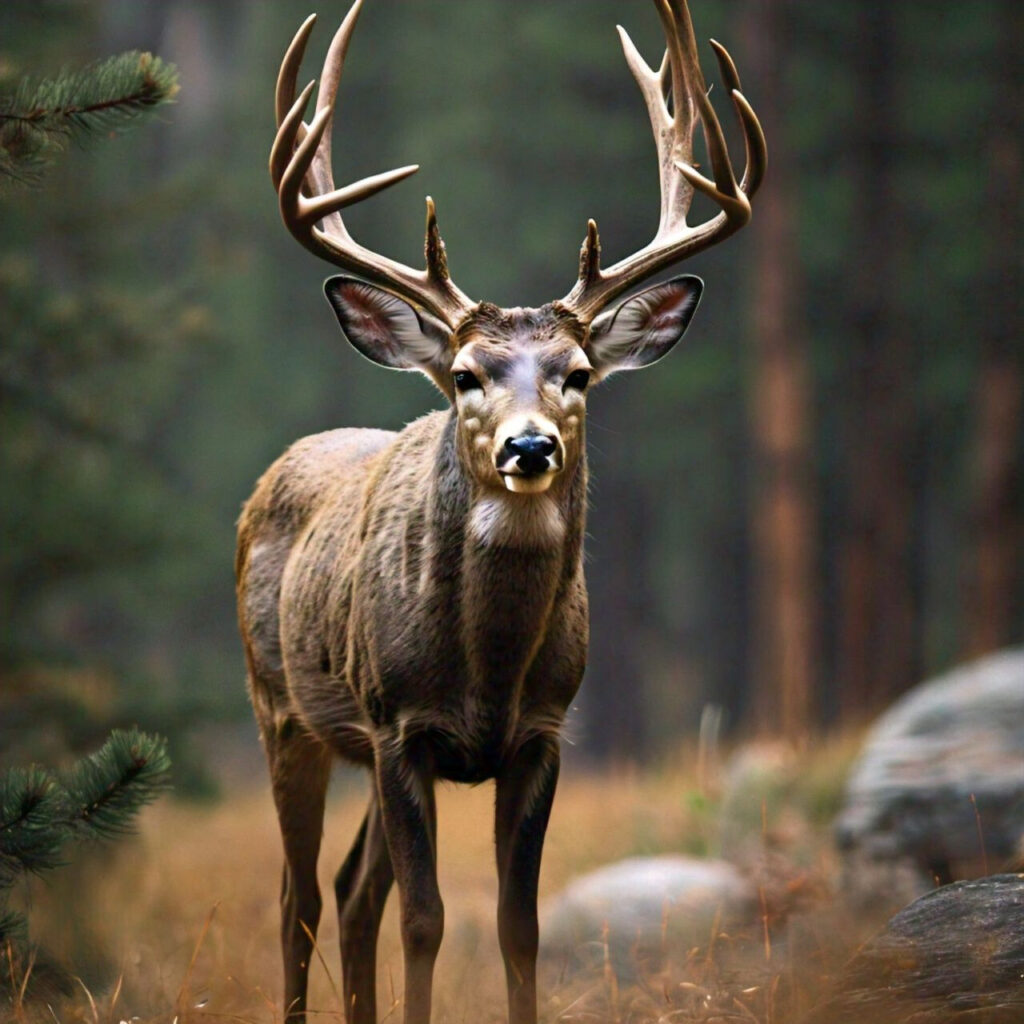

Table of Contents
A Quiet Killer: A Comprehensive Overview of Chronic Wasting Disease
Wyoming Mule Deer and CWD
Moose, deer, elk, and other cervids are susceptible to CWD, a transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE). It causes gradual neurological deterioration by attacking the animal’s central nervous system. Animals that contract the infection become malnourished, listless, and uncoordinated, which finally results in death.
As of right now, there is no vaccination or cure for CWD.
Wyoming Mule Deer and CWD
The disease-causing prions are extraordinarily hardy, able to linger in the environment for years and possibly spread to healthy animals by contaminated water, soil, or contact with human fluids.
Ground Zero: The Infected Herds in Wyoming
Wyoming Mule Deer and CWD
Since the middle of the 1980s, Wyoming has struggled with CWD. The southern herds have the highest prevalence rates of the disease, suggesting that it is especially concentrated in some areas. Research has revealed that in some places, infection rates are over 20%, which is quite alarming for the sustainability of the community.
Such high infection rates have grave repercussions.
Wyoming Mule Deer and CWD
Mule deer survival rates may be considerably reduced by CWD, according to research, which could result in a population collapse. Long-term viability of infected herds may be jeopardized if they are unable to reproduce at a rate high enough to compensate for losses.
A Hurry to Find Answers
It is imperative that something be done about this issue immediately.
- Scientists and managers of wildlife are concentrating their efforts in the following important areas:
- Increased Surveillance: In order to determine the precise presence of CWD and monitor its transmission, more thorough testing of deer populations is essential.
Investigating Therapies and Management: It would be revolutionary to develop a CWD vaccination or therapy. Although there is still much to be discovered, ongoing study shows promise.
Strategic Management: To lessen disease transmission among herds, deer herd management strategies like targeted culling of diseased animals are being investigated.
Nonetheless, there is ongoing discussion on the morality and efficacy of these actions.
Wyoming Mule Deer and CWD
Public Awareness: It is crucial to inform the public and hunters alike about CWD. The disease can be contained faster if sick animals are identified and reported as soon as possible.
Outside of Wyoming: A More General Concern
Although the focus of the current issue is in Wyoming, mule deer populations across their range are at risk from chronic disease disease (CWD).
Wyoming Mule Deer and CWD
To stop the illness from spreading to new regions, there must be heightened awareness and cross-state cooperation.
An enormous ecological and societal damage would result from the possible extinction of Wyoming’s mule deer herds. These creatures are not just recognizable icons; they are also essential to the ecology of the state.
Predator populations and the general health of the rangelands would be negatively impacted by their reduction.
A Request for Action: Preserving a Western Treasure
The mule deer population in Wyoming faces uncertain futures.
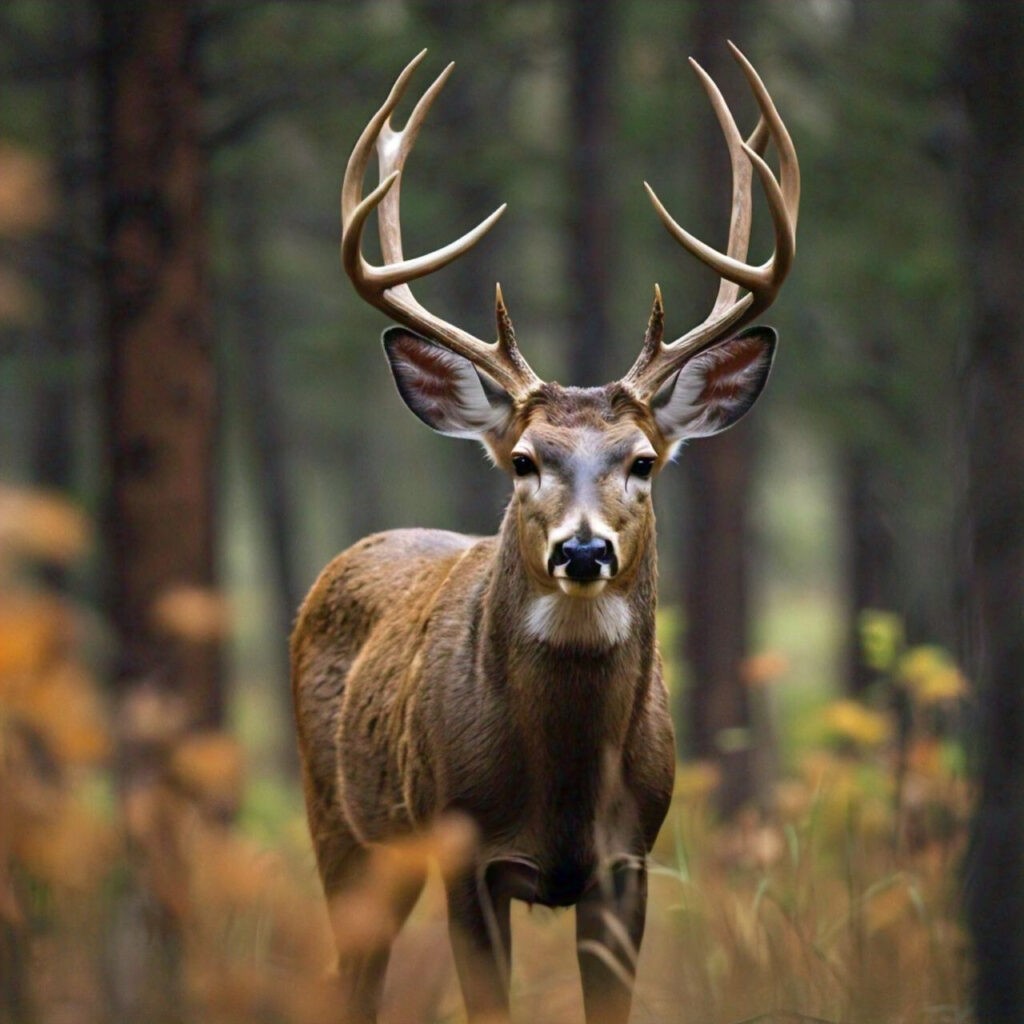

We can assist reverse the trend of CWD by funding research initiatives, promoting sensible management practices, and raising public awareness.
Together, we can make sure that these amazing creatures are around to enjoy the sagebrush plains for many more years to come.

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.






















































Recent Comments