Conquering Cancer: How Combination Therapy is Changing the Game
Share IT

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.
Categories
Combination Therapy
Fighting Cancer: The Effectiveness of Combination Treatments
Given the complexity and cleverness of the disease, cancer treatment must be as planned. Presenting combination therapy, the foundation of contemporary oncology. This blog explores the many forms, advantages, and current developments of combination therapy, delving into their subtleties.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!Table of Contents
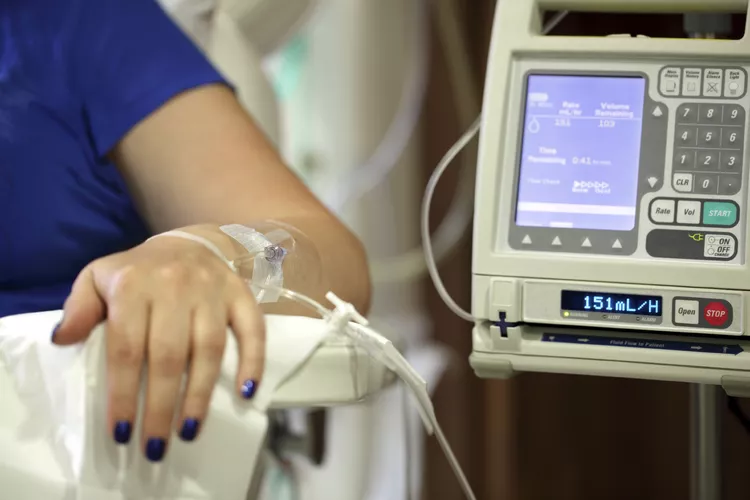
Why Mix Up Your Treatments?
Combination Therapy
Conventional cancer therapies, such as radiation, chemotherapy, and surgery, have shown positive results. But resistance development in cancer cells is well-known. Combination therapy uses a multifaceted approach to address this problem. This is how it operates:
- Targeting Several Pathways: In order to survive and proliferate, cancer cells depend on complex networks of biochemical pathways. Combination therapy makes it more difficult for cancer to become resistant to a single treatment by using medications or methods that target several pathways at once.
- Synergy and Additive Effects: Some combinations have the potential to produce an action that is more potent when taken as a whole than when taken separately. Furthermore, certain combinations have an additive impact that raises the effectiveness of treatment even further.
- Decreased Risk of Resistance: Combination therapy lowers the chance that resistant populations may arise by attacking cancer cells via a variety of methods.
Exposition of the Arsenal: Categories of Combination Treatments
Combination Therapy
Combination therapy’s adaptability is what makes it so beautiful. These are a few typical kinds:
- Chemotherapy Combinations: To produce a more powerful onslaught, several chemotherapeutic medications with different modes of action are combined.
- Chemo-radiation treatment: is the combination of radiation therapy and chemotherapy medications. Radiation therapy can improve results by increasing the susceptibility of cancer cells to chemotherapy.
- Combinations of Immunotherapy: To enhance immune response, immunotherapy medications that use the body’s immune system to combat cancer can be taken in addition to other treatments like chemotherapy or targeted therapies.
- Adjuvant/Neoadjuvant Therapy: In order to eradicate microscopic cancer cells and enhance overall results, surgery may be coupled with chemotherapy or radiation therapy either prior to (neoadjuvant) or subsequent to (adjuvant) surgery.
Streamlining the Method: Customising Sets
Customisation is key to combination therapy’s success. When creating a treatment plan, oncologists take into account a number of important variables, including the patient’s general health, the type and stage of the cancer, and possible adverse effects. Genetic testing advances have made targeted therapy possible, which take advantage of particular mutations that fuel the spread of cancer. This opens the door for combination strategies that are more individualised and successful.
Getting Around: Obstacles and Things to Think About
Even while combination therapy has a lot of promise, there are drawbacks as well:
- Increased Side Effects: The number of side effects associated with combining therapies may increase. To guarantee the wellbeing of patients, careful administration and observation are essential.
- Treatment Complexity: Careful preparation and teamwork among medical experts are necessary when coordinating several treatment methods.
- Cost considerations: Since combination therapy can be costly, it is important to have strong healthcare systems in place to guarantee that all patients can receive it.
Combination therapies’ future: a glimmer of hope
Combination therapy approaches are continually being improved and innovated by researchers. This is a sneak peek at the fascinating future:
- Innovative Drug Combinations: Current studies investigate the effectiveness of combining medications from the current generation with well-proven treatments to treat diseases that were previously incurable.
- Using the Immune System: Using immunotherapies in conjunction with other treatments offers a great deal of potential for long-term cancer control.
- Precision Medicine: Developments in personalised medicine will enable the creation of even more specialised combination treatments based on the genetic profiles of specific patients.
To sum up, combination therapy is evidence of how cancer treatment has changed throughout time. We can improve patient outcomes and outwit cancer’s resistance by utilising a broad range of therapeutic techniques. In the battle against this powerful illness, combination therapy provides a glimmer of hope as science opens up new avenues.

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.






















































Recent Comments