Demystifying Diabetes Medications: Pills vs. Injections for Effective Blood Sugar Control
Share IT

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.
Categories
Diabetes Medication Options
Understanding Oral and Injectable Treatments for Diabetes Management: A Guide to the Medication Maze
Medication is frequently used in conjunction with lifestyle changes to treat diabetes. Insulin injections and oral pills are the two primary types of diabetic therapy covered in this book. Knowing these choices gives you the ability to collaborate with your physician to choose the ideal course of action for your particular requirements.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!Table of Contents
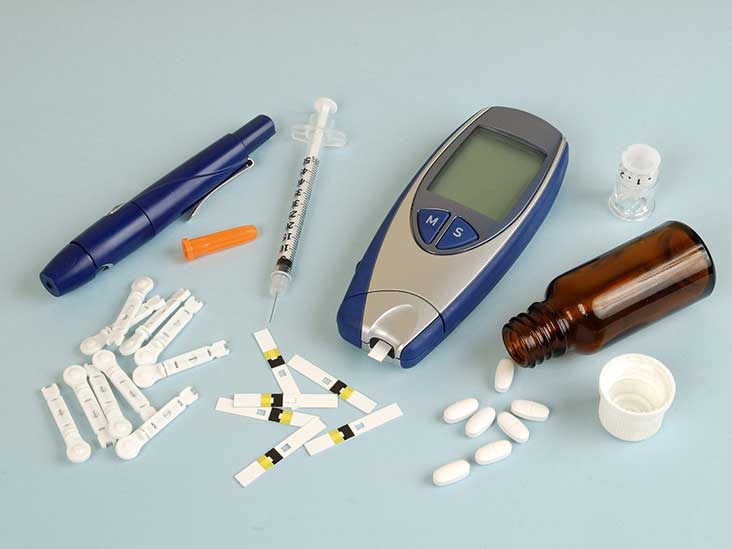
Diabetes Medication Taken Orally:
Diabetes Medication Options
These drugs, which are usually taken as pills, reduce blood sugar levels in a variety of methods. These are a few typical kinds:
- For most people with type 2 diabetes: metformin is the recommended first-line drug. It decreases the liver’s synthesis of glucose and increases insulin sensitivity.
- Sulfonylureas: These induce the production of more insulin by the pancreas.
- Meglitinides: They function similarly to sulfonylureas, although they do so more quickly and for a shorter amount of time.
- DPP-4 Inhibitors: Assist in enhancing insulin synthesis and lowering the pancreas’ release of glucagon, a hormone that elevates blood sugar.
- SGLT2 Inhibitors: Prevent the kidneys from reabsorbing glucose, allowing extra sugar to be eliminated through the urine.
Advantages of Oral Drugs:
Diabetes Medication Options
- Convenient: Simple to handle and take.
- Non-invasive: No needles are needed.
- A Suggestion for Diabetes in its Early Stages: can occasionally be successful in controlling blood sugar, especially in the early stages of type 2 diabetes.
Possible Things to Think About:
Diabetes Medication Options
- Side Effects: Possible side effects include weight gain, hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), and intestinal problems.
- Dosage Modifications: As the illness worsens, dosage modifications may be necessary.
- Not for Everyone: Not Ideal for All Not suitable for people who need strict blood sugar regulation or for all forms of diabetes.
Insulin for Injection:
Diabetes Medication Options
Your body uses the hormone insulin, which is present naturally, to help it use glucose for energy. For certain forms of diabetes, injectable insulin is a mainstay treatment that can be combined with other drugs.
Insulin Types That Are Injectable:
Diabetes Medication Options
- Fast-acting: After meals, it lowers blood sugar levels swiftly.
- Short-acting: To control blood sugar rises after meals, use this medication prior to meals or snacks.
- Intermediate-acting: Offers blood sugar control that lasts longer throughout the day.
- Long-acting: Provides long-lasting blood sugar regulation; frequently used at night.
Advantages of Insulin Injectable:
Diabetes Medication Options
- Effective Blood Sugar Control: Precise and effective blood sugar management is provided by this method, which is especially helpful for people with type 1 and severe type 2 diabetes.
- Flexibility: To fulfil specific needs, several kinds of insulin can be blended.
Possible Things to Think About:
Diabetes Medication Options
- Injections: Needs injections, which some patients may find difficult.
- Injection Technique: For best outcomes, use the appropriate injection technique.
- Hypoglycemia Risk: A higher risk of hypoglycemia need close observation, dosage adjustments for insulin, and dietary modifications for carbohydrates.
Selecting the Appropriate Drug:
Your lifestyle, specific health demands, and the type and stage of your diabetes will all determine which medicine is best for you. Find the best drug or combination of drugs for the best blood sugar control by consulting with your doctor frequently.
Extra Things to Think About:
- Frequent Monitoring: For people on insulin or oral medicines, blood sugar monitoring is essential.
- Changes in Lifestyle: Medicine works best when taken in conjunction with a balanced diet, frequent exercise, and weight control.
- Long-Term Management: Since diabetes is a chronic illness, it calls for constant communication and necessary modifications to your treatment plan.
Recall:
It’s not only you who is managing your diabetes. You may effectively control your blood sugar and lead a fulfilling life with good medication management, a healthy lifestyle, and a cooperative relationship with your physician.
Notice: This information is not meant to replace expert medical advice; rather, it is meant mainly for general awareness. Always discuss your particular case with your doctor, and heed their advice.

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.






















































Recent Comments