Understanding Your Lungs: COPD Diagnosis with Spirometry & PFTs (COPD Lung Function Tests Explained)
Share IT

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.
Categories
COPD Lung Function Tests Explained
Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs): Taking Stock of Your Lungs in COPD
Breathing difficulties are a hallmark of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), a lung disorder that progresses over time. PFTs, or pulmonary function tests, are essential for both detecting and treating COPD. These non-invasive tests evaluate many facets of lung function, offering important data to influence treatment choices and track the course of the illness. This blog post explores the various PFTs, including as spirometry, lung volumes, and diffusion capacity, that are frequently used to diagnose COPD.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!Table of Contents
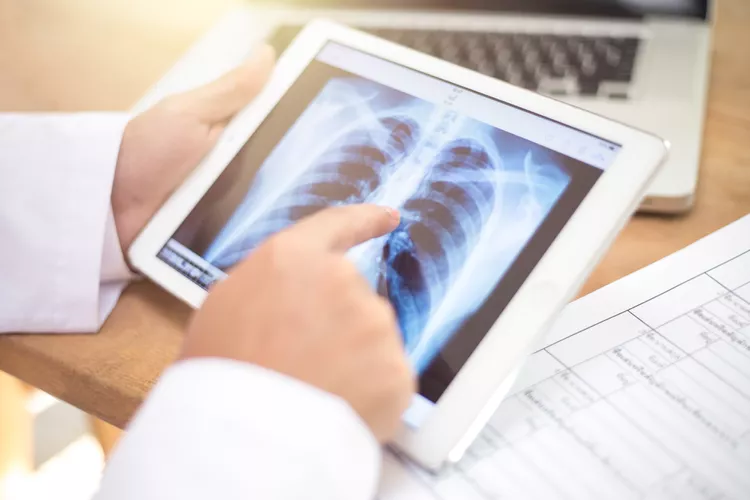
PFTs, or pulmonary function tests, what are they?
COPD Lung Function Tests Explained
PFTs are a battery of examinations used to gauge lung function. They evaluate:
- Lung volumes: The volume of air that can fit inside your lungs.
- Airflow rates: The rate at which air enters and exits your lungs.
- Gas exchange: The rate at which carbon dioxide is expelled from your body and oxygen is absorbed.
COPD Lung Function Tests Explained
A qualified technician usually conducts PFTs in a specialist laboratory. These tests are generally safe and painless, though they can cause some mild discomfort.
PFT types used to diagnose COPD
COPD Lung Function Tests Explained
To identify and track COPD, various PFT types are used, each of which offers unique data:
- Spirometry
The most popular and important PFT for diagnosing COPD is spirometry. It calculates airflow rates, specifically:
- The entire volume of air you can forcibly exhale after taking a deep breath is known as your forced vital capacity, or FVC.
- The amount of air you can forcefully exhale in the first second of an FVC maneuver is known as the forced expiratory volume in one second, or FEV1.
COPD Lung Function Tests Explained
A FEV1 to FVC ratio: This ratio aids in identifying the COPD characteristic of airflow restriction. This ratio is usually greater than 70% in healthy persons. A reduced ratio indicates a COPD-related airflow restriction.
Test for Reversibility of Bronchodilators:
COPD Lung Function Tests Explained
In this test, spirometry is repeated following the administration of a bronchodilator drug, which relaxes airways. When bronchodilators are used, an improvement in FEV1 may indicate asthma rather than COPD.
- Tests of Lung Volume:
The entire amount of air that your lungs can hold is measured via lung volume testing. Among these tests are:
- The total quantity of air that your lungs can hold following a maximal inhalation is known as total lung capacity, or TLC.
- After completely exhaling, the amount of air in your lungs is known as residual volume, or RV.
- Lung volumes may be lowered in COPD as a result of air trapping in the lungs.
- Carbon Monoxide Diffusion Capacity (DLCO):
This examination gauges how well oxygen enters your bloodstream from your lungs. The ability of oxygen to diffuse across the lung membrane may be compromised in certain COPD instances.
How Do PFT Findings Aid in COPD Management?
COPD Lung Function Tests Explained
PFT findings are essential for controlling COPD since they:
- Verifying Diagnosis: Spirometry shows airflow restriction, which aids in the diagnosis of COPD.
- Assessing Disease Severity: FEV1, which measures the degree of airway obstruction, can be used to assess the severity of COPD.
- Tracking the Progression of the Disease: Frequent PFTs enable medical professionals to track alterations in lung function over time.
- Evaluation of Treatment Response: By monitoring variations in airflow rates, PFTs can assist in evaluating the efficacy of treatment programs.
Please take note that a healthcare provider should always evaluate PFT findings in conjunction with other clinical factors and symptoms.
Managing COPD: Going Beyond PFTs
COPD Lung Function Tests Explained
PFTs are an important tool, but they don’t fully convey what it’s like to have COPD. Additional elements affecting well-being are as follows:
- Symptoms: The quality of life is greatly impacted by coughing, exhaustion, and dyspnea.
- Co-morbidities: A large number of COPD patients also have other medical disorders that need to be managed holistically.
- Functional Status: Retaining one’s independence and standard of living requires the capacity to carry out daily tasks.
In addition to PFTs, open communication on your symptoms, worries, and general health is crucial for achieving the best possible management of your COPD.
Patients who are aware of the importance PFTs play in the diagnosis and treatment of COPD can take an active role in their care and collaborate with their healthcare professionals to get the best results.

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.






















































Recent Comments