Diabetic Gastroparesis: Why Won’t My Stomach Empty?
Share IT

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.
Categories
Diabetic Gastroparesis
Managing a Sluggish Digestive System: Comprehending Diabetic Gastritis
Controlling blood sugar levels is a lifelong priority for diabetics. Digestion is one of the numerous biological processes that diabetes can impact. A problem known as diabetic gastroparesis develops when high blood sugar levels harm the stomach’s muscles and nerves, delaying the emptying of the stomach’s contents. This may result in a number of painful symptoms as well as dietary difficulties.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!Table of Contents
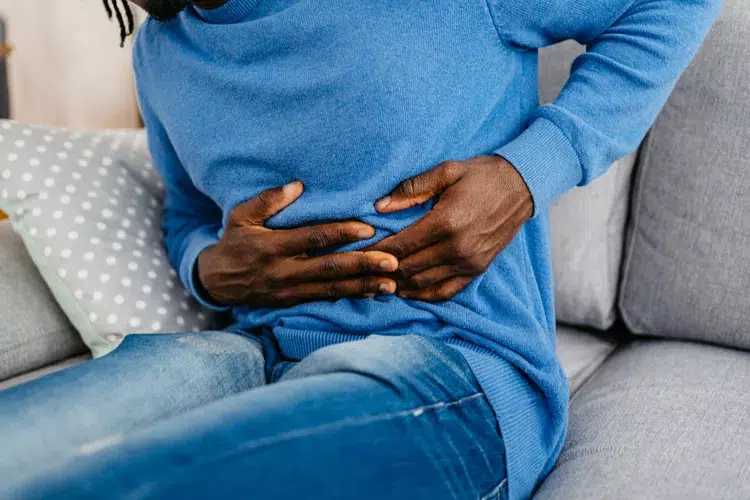

Exposing the Mechanism: How Diabetes Resulted in Gastroplasty
Diabetic Gastroparesis
Diabetes with persistently high blood sugar levels can cause gastroparesis in a number of ways, including:
- Damage to the nerves: that govern the stomach’s muscles can result from high blood sugar, making it more difficult for the stomach to contract and propel food forward. This condition is known as neuropathy.
- Delayed gastric emptying: Food stays in the stomach longer than usual due to weakening stomach muscles, which causes discomfort, nausea, and sensations of fullness.
- Problems with the oesophagus: Sometimes, nerve injury can also impact the oesophagus, which is the muscular tube that connects your mouth to your stomach, making swallowing difficult.
A Range of Indications: Identifying Gastrodoresis
Diabetic Gastroparesis
Many symptoms, such as the following, can be present with diabetic gastroparesis:
- Early satiety: Having a rapid sense of fullness even after consuming a little quantity of food.
- Vomiting and nausea: Unprocessed food particles may re-enter the stomach, causing vomiting and nausea.
- Upper abdominal pain or discomfort: After eating, one may experience bloating or a fullness in the upper abdomen.
- Weight loss: Unintentional weight loss might result from eating and food absorption difficulties.
- Appetite loss: Eating can cause discomfort, which can result in a decrease in appetite.
- Blood sugar swings: It might be challenging to control blood sugar levels when there is a delayed stomach emptying.
It’s crucial to remember that other illnesses may possibly be the source of similar symptoms. It’s essential to see your doctor for a correct diagnosis.
When to Get Assistance: Prompt Action Is Crucial
Diabetic Gastroparesis
See your doctor right away if you suffer any of the symptoms listed above, especially if you have nausea, vomiting, or trouble keeping food down. Your quality of life can be enhanced and consequences can be avoided with early diagnosis and treatment.
Handling Gastroparesis: A Comprehensive Method
Diabetic Gastroparesis
Although diabetic gastroparesis has no known cure, there are a number of techniques that can help control symptoms and enhance your quality of life:
- Dietary changes: Easier digestion can be achieved by eating small, frequent meals that include easily digested foods.
- Nutritional support: To guarantee sufficient nutrient intake in extreme situations, tube feeding or liquid nutritional supplements may be required.
- Medication: It can be beneficial to take medications that manage nausea and vomiting or that help induce stomach contractions.
- Blood sugar regulation: Sustaining appropriate blood sugar regulation is essential for the general well-being of diabetics and may tangentially alleviate symptoms of gastroparesis.
- Injecting Botox: into the pyloric sphincter (the muscle near the stomach’s exit) may assist it relax and enhance the process of emptying the stomach in certain circumstances.
Managing Your Gastroparesis Well: Sustaining a Healthful Way of Life
Diabetic Gastroparesis
Apart from the previously discussed tactics, various lifestyle adjustments can enhance general well-being in individuals with gastroparesis:
- Control your stress: Anxiety can exacerbate stomach issues. Yoga and meditation are examples of relaxation exercises that can be helpful.
- Keep yourself hydrated: It’s critical to consume lots of water throughout the day, particularly if you feel queasy or throw up.
- Steer clear of smoke: It can exacerbate the symptoms of gastroparesis and harm your health in general.
- Frequent exercise: Leading an active lifestyle helps enhance general health and digestion. It is advised to engage in moderate-intensity exercise for 30 minutes on most days of the week.
- Support Teams: Making a connection with others who are aware of the difficulties associated with diabetic gastroparesis can be a source of inspiration and emotional support.
A Preview of What’s to Come: The Treatment of Gastropteresis in the Future
Diabetic Gastroparesis
Researchers are always looking at novel ways to treat diabetic gastroparesis. Promising research fields include:
- Electrical stimulation: Applying electrical impulses to stimulate the vagus nerve, which regulates stomach function, may provide comfort.
- Novel drugs: Research is being done on novel medications that focus on particular elements of the disease process.
Concluding Remarks: Leading a Contented Life Despite Gastroplasty
Diabetic Gastroparesis
Although diabetic gastroparesis can be difficult to manage, you can still have an active and fulfilling life with it if you make the right lifestyle changes. You may manage your symptoms and preserve general health by consulting with your doctor, coming up with a treatment strategy that works for you, and forming healthy behaviours. Recall that you are not travelling alone. To assist you live a healthy and well-managed life with diabetic gastroparesis, there are tools and support available.

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.






















































Recent Comments