Diabetic Eye Disease: Warning Signs, Prevention, and Protecting Your Vision
Share IT

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.
Categories
Diabetic Eye Disease
Diabetes and Diabetic Retinopathy: Protecting Your Vision
One of the main causes of blindness in adults in their working years is diabetic retinopathy. It is a diabetic complication that develops when blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive layer in the back of the eye that is responsible for vision, are harmed by high blood sugar levels. Diabetic retinopathy frequently advances silently at first, with no symptoms. To stop vision loss, however, early detection and treatment are essential.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!Table of Contents
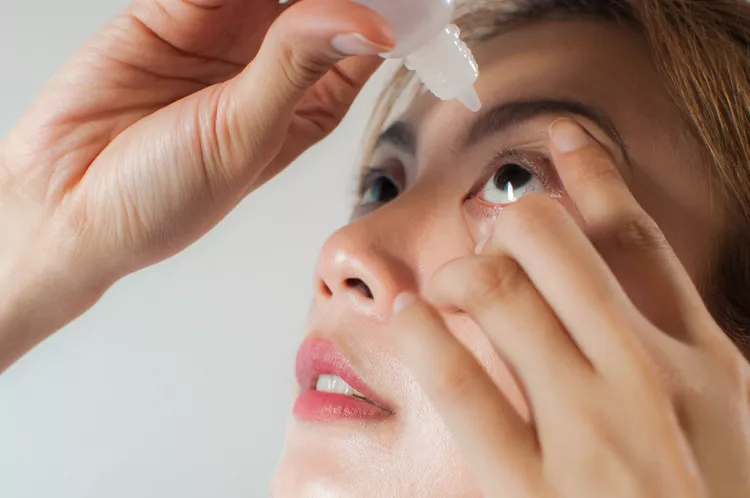

Exposing the Enigma: How Diabetes Leads to Retinopathy?
Diabetic Eye Disease
There are two basic ways that diabetes with persistently elevated blood sugar levels might damage the fragile blood vessels of the retina:
- Blood vessel weakening: High blood sugar causes the retinal blood vessels’ walls to deteriorate over time, allowing fluid or blood to seep into the retina.
- Abnormal blood vessel growth: The retina’s blood vessels may grow abnormally in an attempt by the body to make up for the damage. Nevertheless, the fragility and weakness of these new veins raises the danger of bleeding and visual issues even more.
Diabetic Retinopathy Stages: A Range of Intensities
Diabetic Eye Disease
There are various stages that diabetic retinopathy goes through, each with a different severity:
- Background retinopathy: This is the initial stage and is frequently asymptomatic. Mild edoema might result because fluid or blood leaks from tiny blood vessels in the retina.
- Macular edoema: Vision can become distorted or hazy when fluid builds up in the macula, the area of the retina in the centre that is responsible for clear central vision.
- Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR): In this advanced stage, the retina’s surface is covered in abnormally growing new blood vessels as a result of the body’s reaction to damaged blood vessels. The translucent, jelly-like liquid that fills the centre of the eye, the vitreous gel, may flow into these delicate arteries, resulting in floaters, or dark spots in your vision. In extreme situations, scar tissue may develop, exerting pressure on the retina and possibly resulting in retinal detachment, a dangerous consequence that may result in irreversible blindness.
Knowing the Warning Signs and Knowing When to Get Help
Diabetic Eye Disease
Many cases of early diabetic retinopathy are asymptomatic. But if the illness worsens, you could encounter:
- hazy vision
- Having spots or floaters in your field of view
- distorted or wavering eyesight
- Having trouble seeing colours
- abrupt loss of vision
Diabetic Eye Disease
It is imperative that you make an appointment with your eye doctor right away if any of these symptoms occur.
Safeguarding Your Vision: Prompt Identification and Handling Techniques
Diabetic Eye Disease
Early identification via routine eye exams is essential to preventing diabetic retinopathy-related visual loss. What you can do is as follows:
- Plan thorough eye exams: Even if they do not have any vision issues, people with diabetes should get a dilated eye exam at least once a year.
- Keep your blood sugar under control: The best strategy to stop or slow the onset of diabetic retinopathy is to keep your blood sugar levels within the target range.
- Control your blood pressure: High blood pressure might make diabetic retinopathy worse.
- Healthy living decisions: Eating a balanced diet, exercising frequently, and maintaining a healthy weight can all improve general health, including your eyesight.
Options for Treatment: Taking Care of Various Stages
Diabetic Eye Disease
The severity and degree of diabetic retinopathy determine the course of treatment. Here are a few typical methods:
- Laser surgery: To stop additional bleeding and preserve eyesight, aberrant new blood vessels can be destroyed or leaky blood vessels can be sealed using laser photocoagulation.
- Injections into the eyes: By inhibiting the formation of aberrant blood vessels, anti-VEGF drugs injected into the eyes can help lessen macular edoema.
- Vitrectomy: Surgery may be required to remove blood and restore eyesight in cases of significant bleeding in the vitreous gel.
Managing Diabetes Well: Safeguarding Your Vision
Diabetic Eye Disease
You can lower your risk of diabetic retinopathy-related vision loss by following your doctor’s instructions, getting regular eye exams, and making proper diabetes management a priority. Here are a few more pointers:
- Become knowledgeable: Being aware of the dangers associated with diabetic retinopathy enables you to take preventative measures to preserve your vision.
- Be open with one another: Talk about any visual issues with your diabetes care team and eye doctor.
- Retain a cheerful attitude: In most situations, vision loss can be prevented with early detection and treatment. You can have a full and active life with diabetes if you manage it properly.
Diabetic Eye Disease
Diabetic retinopathy is a dangerous side effect that can be avoided. You can protect your vision and have a healthy future by managing your diabetes and cooperating with your healthcare team.

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.






















































Recent Comments