Don’t Ignore Your Neck: Carotid Artery Disease & Stroke Prevention
Share IT

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.
Categories
Carotid Artery Disease Stroke Risk
Carotid Artery Disease and Stroke Risk: A Silent Threat
Stroke is one of the world’s leading causes of disability and death. It is frequently associated with restricted or clogged arteries that feed blood to the brain. The primary blood vessels in your head and neck, the carotid arteries, are the target of carotid artery disease (CAD). This blog post explores the relationship between CAD and stroke risk, describing how the illness can subtly raise your risk of having a stroke and providing prevention and treatment options.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!Table of Contents
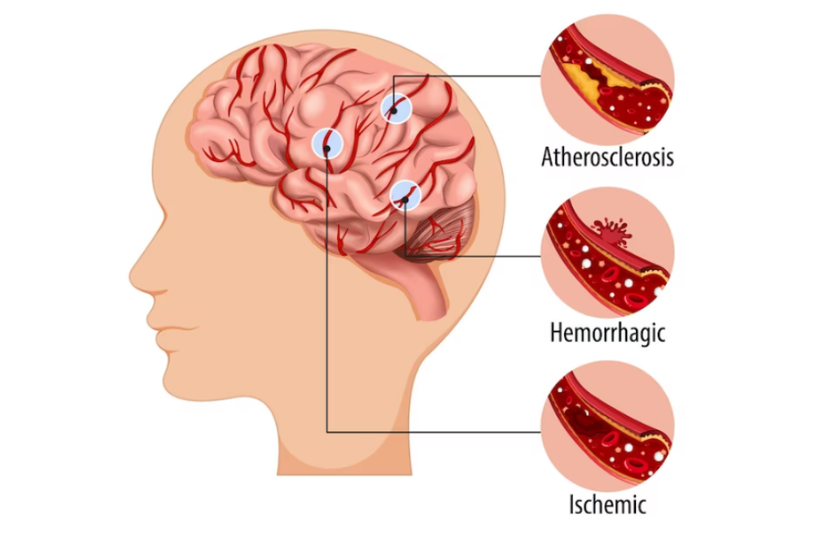
Knowing the Function of Carotid Arteries
The body’s main blood vessels that supply blood to the face and brain are called carotid arteries, and they are situated on either side of your neck. These arteries transport blood from the heart that is high in oxygen, which provides vital nutrients to the brain’s cells and maintains their functionality.
Carotid Artery Disease (CAD): What is it?
Carotid Artery Disease Stroke Risk
Plaque, a fatty deposit, develops on the inner walls of the carotid arteries and causes CAD. The arteries get narrowed by this plaque accumulation, limiting blood flow to the brain. In extreme circumstances, a blood clot may develop inside the plaque, which may break free and go to the brain, obstructing an artery and resulting in a stroke.
Silent Danger: Until a major blockage occurs, CAD frequently advances silently, with no symptoms. For this reason, it’s critical to understand your risk factors and, if needed, get screened.
How Does CAD Raise the Chance of Strokes?
Carotid Artery Disease Stroke Risk
There are two ways that CAD raises your risk of stroke:
- Decreased blood flow: The carotid arteries get narrowed by plaque accumulation, which lowers the volume of blood that reaches the brain. Particularly when paired with additional risk factors like high blood pressure, this can result in stroke.
- Blood clot formation: Roughened plaque surfaces inside arteries can serve as a breeding ground for blood clots. A clot can obstruct an artery and result in a stroke if it breaks free and moves to the brain.
The Carotid Artery Disease Risk Factors
Carotid Artery Disease Stroke Risk
The following variables raise your chance of developing CAD:
- Age: As people age, their risk of CAD rises.
- High blood pressure: Unchecked hypertension weakens the walls of blood vessels and encourages the accumulation of plaque.
- High cholesterol: The development of plaque is facilitated by high levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol.
- Smoking: Smoking raises the risk of blood clotting and destroys blood vessels.
- Diabetes: This illness can lead to plaque accumulation and blood vessel damage.
- Family history: Your risk is increased if you have a close family who has CAD.
- Obesity: Carrying too much weight increases the risk of high blood pressure and other CAD risk factors.
CAD Symptom Recognition (Although Often Silent)
Carotid Artery Disease Stroke Risk
Even while CAD is generally undetected, certain people may encounter:
- Neck pain or tenderness: Though rare, neck pain or tenderness may arise with severe constriction.
- Attacks with transient ischemia (TIA): A “mini-stroke” that appears like a stroke but goes away in a day or two could be the result of a carotid artery blockage.
Making a Carotid Artery Disease Diagnosis
Carotid Artery Disease Stroke Risk
A number of examinations can identify CAD, such as:
- Carotid artery ultrasound: This non-invasive procedure creates pictures of the carotid arteries and evaluates the amount of plaque accumulation using sound waves.
- Carotid angiogram: This X-ray method shows the carotid arteries’ blood flow by using a contrast dye.
- CT scan or MRI: The carotid arteries and associated structures can be seen in great detail with a CT scan or MRI.
The best test will be suggested by your doctor depending on your particular risk factors and symptoms.
Stroke Prevention with CAD Management
Carotid Artery Disease Stroke Risk
Stroke prevention depends on the early diagnosis and treatment of CAD. The following are some tactics:
- Lifestyle changes: You can dramatically lower your risk of CAD by maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and giving up smoking.
- Medication: Statins are one type of medication that can help lower cholesterol and lessen plaque accumulation.
- Blood pressure control: Preventing more damage to blood vessels is made possible by medications used to treat excessive blood pressure.
- Endarterectomy or carotid artery stenting: In extreme situations, minimally invasive techniques such as endarterectomy, which involves surgically removing the accumulation of plaque, may be required.
In summary, prevent a stroke from stealing your future.
Carotid Artery Disease Stroke Risk
A quiet menace that might raise your risk of stroke is carotid artery disease. You can proactively prevent this debilitating condition by being aware of potential signs, knowing your risk factors, and getting the necessary screening. Recall that maintaining your mental health and avoiding stroke depend on the early detection and treatment of CAD.

Launch Your Dream Website with Us!
Click Here to Get in touch with Us.






















































Recent Comments